The importance of email security does not need to be proven. It is the reason why Europe established data privacy and security laws, leading to the well-known GDPR.
A 2024 study showed that 94% of surveyed organizations had fallen victim to a phishing attack in the last 12 months!
More shocking, ransomware attacks increased by 84% in 2023, with an average ransom amount of USD 400,000 and recovery costs of USD 1.8 million.
However, as we’ll explore in this guide, email security is not just a corporate matter. As an individual, there are many reasons why you should take your email security seriously. So without further ado, let’s dive in.
What is Email Security?
Let’s get right down to business.
Email security is the practice of protecting email accounts and their contents from unauthorized access, leaks, or compromise.
Email security can therefore include the following:
- tools such as antivirus software, encryption methods, etc;
- specific policies and best practices to follow.
The ultimate goal of email security is to guarantee (as much as possible) that an email account and its contents do not fall into the wrong hands. At a corporate level, this means protecting trade secrets, company data such as sales figures, and internal data such as employee remuneration.

However, email security is not limited to companies. At a personal level, there are 2 main reasons why you should protect your emails from prying eyes:
- Personal information: your email account contains a wealth of private information that you want to keep private, such as your address and phone number, medical appointments, online purchases and subscriptions, travel plans, etc. In the wrong hands, these data points can become a tool for ransoms.
- Advertising. The more companies know about you, the better they can sell you products and services that you don’t want or need. Email security therefore protects you against unwanted advertising.
The Evolution of Email Security Through the Years
In the 1980s, developers adopted the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) to send emails.
At that time, only a small number of institutions used the Internet, so security was not a primary concern. Developers did not design the protocol to protect email content or verify the sender’s identity.
As email usage grew and the Internet expanded, the lack of security in SMTP became a significant issue. By the 1990s, spam emails and email fraud were rampant. There was a clear need for better security protocols to protect email communications.
SSL and TLS
In the mid-1990s, two new protocols were developed to improve the security of communications over the Internet:
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL): this protocol allows for the encryption of data, making it difficult for unauthorized parties to read the content of emails.
- Transport Layer Security (TLS): this protocol later supplanted SSL by offering improved security and has become the standard for encrypting emails in transit.
When you see “https://” in your browser, that means SSL/TLS is being used to secure the connection.
SPF, DKIM and DMARC
While protecting email in transit is important, another key aspect of email security was yet to be looked at.
When someone sends you an email from a given address, how do you know they are who they say they are?
If you receive an email from your brother’s email address, how can you say for sure that your brother sent that email? This tactic, known as email spoofing, is a serious social engineering attack. To combat it, developers created protocols to verify the identity of email senders. Here are the 3 major ones in application today:
- SPF: Sender Policy Framework checks if an email is sent from an authorized server. When an email is received, the receiving server checks the SPF record of the sender’s domain to ensure the email comes from an authorized source.
- DKIM: DomainKeys Identified Mail adds a digital signature to emails, which can be verified by the receiving server to ensure the email has not been tampered with during transit. This signature is unique to the sender’s domain, providing further assurance of authenticity.
- DMARC: Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance builds on SPF and DKIM, allowing domain owners to specify how emails that fail SPF or DKIM checks should be handled. This helps to protect against phishing attacks by providing a mechanism for email receivers to reject or quarantine suspicious emails.

Beyond SMTP: SMTP STS
As email security advanced, developers introduced SMTP MTA Strict Transport Security (SMTP STS) to address vulnerabilities in email transmission. SMTP STS enforces strict security policies and ensures emails are sent over secure, encrypted connections.
SMTP STS enhances email security by enabling email service providers to publish policies specifying secure transmission requirements. When sending an email, the server checks the recipient domain’s SMTP STS policy to confirm a secure connection. If the connection fails to meet the policy’s standards, the email is not sent, offering strong protection against man-in-the-middle attacks.
However, SMTP STS is not the be-all-end-all fo email security. In particular:
- messages will stay in clear text, from the sender’s device till it reaches the respective sender’s SMTP server (assuming there’s no SSL/TLS in place).
- messages will remain in clear text, from the recipient’s SMTP server till reaching the recipient’s device (assuming there’s no SSL/TLS in place).
- the SMTP server (both on the sender and recipient side) will be able to view the message in clear text.
These gaps are where adversaries will be able to successfully exploit the confidentiality and integrity of emails. In our opinion, end-to-end encryption (E2EE) remains the answer (more on that later in this guide).
Secure Email vs Regular Email: What’s the Difference?
Once an email is sent, it travels through multiple servers before reaching the recipient. During this transit, anyone who intercepts the email can read its content.
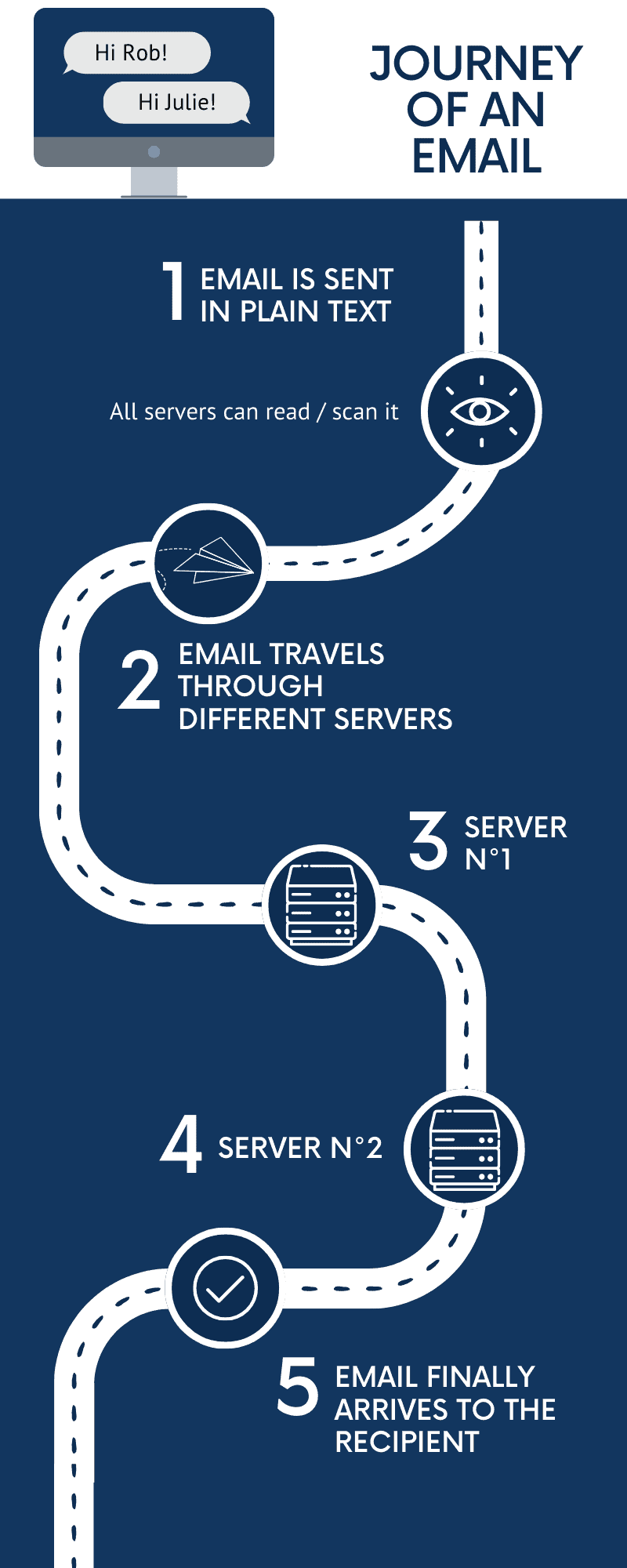
Most regular email services like Gmail, Yahoo, and Outlook prioritize usability and convenience. Features like calendar integrations, smart replies, and advertising-based models are common.
However, this often comes at a security cost:
- data mining and advertising: many free email services scan users’ emails to display targeted advertising. This means they read, process, and use your data to use personalized marketing more effectively.
- server storage: servers typically store regular emails in plain text. If an intruder compromises a server, they can directly access your email content.
While companies might say that they don’t resell your information, how can you be sure?
Looking to create an email account with no phone number required? Check out our latest guide here.
As the saying goes: don’t trust, verify.
Secure email services take a different approach. They emphasize user security and privacy. Here are the standout features:
- End-to-End Encryption (E2EE): With E2EE, your email is encrypted on your device and is only decrypted on the recipient’s device. This means that even if someone intercepts the email during transit, they cannot decipher its content without the decryption key.
- OpenPGP (Pretty Good Privacy): A data encryption and decryption program that provides cryptographic privacy and authentication. Many secure email services use OpenPGP to ensure that emails are private and that they originate from the stated sender.
- Zero-Knowledge Architecture: Some secure email providers operate on a zero-knowledge principle. This means they don’t have access to users’ encryption keys, ensuring that even the service provider cannot read your emails.
- No Data Mining: Secure email services typically refrain from scanning user emails for advertising. They prioritize user trust and data protection over marketing tactics.
On top of this, secure email services will provide additional tools such as symmetric encryption, digital signatures, and more. Check out the following links to learn how Mailfence offers a private and secure email service.
9 Tips on Keeping your Email Account Secure
Choosing a secure email provider such as Mailfence is only the first step. Only privacy and security are a daily commitment, not a one-time ON/OFF switch.
To guarantee maximum email security, follow our 9 tips listed below.
#1: Strong and unique password
Our number one tip is also our most important. And it applies to any account you hold, not just your email.
Cybercriminals do not need elaborate tools to crack your email account, especially when you know that the most common password in 2024 is 123456. There are two major guidelines you should follow to create strong passwords:
- do not use identifying information such as your name or date of birth;
- use at least 12 or 14 characters, but the longer the better.
If you use a password manager, they will generally have an integrated tool that can generate passwords for you. Otherwise, use tools to generate strong passwords if you cannot think of a good one yourself but remember that the length is what you should really care about.
In case of multiple email addresses, make sure to have a specific password for each one. Your password needs to be unique to ensure security. Therefore, if a hacker manages to obtain your password, only one account will be at risk.
#2: Do not share passwords
Never share passwords, neither orally, nor in writing. More importantly, remember that you will never be asked to share a password by email. If someone is claiming they need it, it might be a scam (see point 8 for more info).
#3: Use two-factor authentication (2FA)
By using two-factor authentication, you add another layer of security to protect your email account. First, you log in to your email account by using your username and password. Then, you initiate the second login step. By using a specific application, another security code will be generated to allow account entry.
With 2FA, even if a hacker obtains your password, they still need a second authentication code to access your account.
In other words, it will be impossible for anyone to authenticate to your email account without the TFA code, even if they manage to crack your account password.
Check out this guide to set up 2FA on your Mailfence account. You can use any TOTP application of your choice.
#4: Use end-to-end encryption (E2EE)
End-to-end encryption adds another layer of protection.
When sending an email, you can choose to encrypt the data to protect your email communication. To decrypt the content of your email, the recipient will need a specific key (or a shared password). This way, only the intended recipient will be able to decrypt it.
E2EE can be a bit daunting when you first start learning about it.
That’s why we made a beginner’s guide for you, which you can check out here.
Basically, users have two keys: a public one and a private one. The sender encrypts the message with the recipient’s public key. Only the recipient, with their private key, can decrypt the message.
Just like passwords, you should never share your private key. As the name suggests, this key is and should remain private.
#5: Do not click on a link in an email without investigating
Some hackers have a very sophisticated way to trick you into believing a link is safe when it is not.
As a link might not be what it seems to be, never click on a link in an email before investigating.
First, by resting your mouse on the link without clicking, you will be able to see the URL of the link. Therefore, check if it matches the link typed in the message. If you do not, it is easy for cybercriminals to trick you into clicking on a compromised link.
Hackers can pretend to be someone they are not and ask for sensitive information. Even if what seems to be your bank is asking for personal data, there is no reason for them to ask for it via email. This kind of request should be a warning. Learn more about these kinds of social engineering attacks here.
#6: Avoid connecting apps to your email account
Allowing a third-party app access to your inbox poses a risk, as the app could be compromised. A cybercriminal could access your inbox through the app. All the content of your inbox would then be accessible.
#7: Never access emails when using public Wi-Fi
Another way to protect your email account is by avoiding public Wi-Fi. Although we employ SSL/TLS to protect against MITM attacks, it is always better to avoid connecting to untrusted networks. When possible, use mobile data, even if it means a slower connection.
#8: Stay up-to-date with hackers’ new techniques
Cybercriminals have advanced techniques to trick you into trusting an email you should not. Phishing, spear phishing, … Those funny named techniques might actually be especially harmful if you do not pay enough attention.
The key here is to educate yourself. Stay up-to-date with new forms of attacks by reading news articles.
With the advent of AI, new forms of cyber threats are constantly emerging. Attackers can now easily copy the writing style and tone of somebody you know – or even their voice. That’s why it’s crucial to remain informed.
#9: Always log out
After a long day’s work, log out of your different email accounts. It is especially important when using a public device as anyone could access your private information once you are done.
Nevertheless, logging out is a principled habit to maintain, even from a personal device. Indeed, logging out is the safest way to oblige anyone trying to access your email account to log in. This ensures that even if someone steals your phone or computer, your email account remains secure with your strong, unique password and two-factor authentication (2FA).
To make your life easier, there are many plugins you can install that will automatically log you out when you close your browser.
That’s it for this Guide on Email Security!
There are many email providers out there that claim to be “private and secure”. Even Gmail recently changed its tagline to “Private and secure email at no cost”!
Mailfence is a secure and private email service that provides end-to-end encryption email using OpenPGP and digital signing features. All operations involving private keys and email bodies occur only after the user unlocks the private key using a passphrase known exclusively to them.
For a detailed analysis of the level of protection offered by Mailfence, you can check out this Knowledge Base article.
No email provider can claim to be 100% secure – and there will always be trade-offs. We like to be open about ours so that you can make an informed decision. If you have any questions, feel free to reach out to us at support@mailfence.com
Further reading:
End-to-End Encryption. What Is It and How Does It Work?
Symmetric Encryption: The Easiest Way to Encrypt an Email
Steps To Take When Your Email Is Hacked
What is Email Security? FAQ
Email security involves protecting email accounts and contents from unauthorized access, leaks, or compromise. It’s essential to safeguard personal information, prevent data breaches, and block phishing attacks that could lead to identity theft or financial loss.
Use strong, unique passwords for each account, enable two-factor authentication (2FA), and avoid clicking on unverified links in emails. Additionally, use end-to-end encryption for sensitive communications and avoid accessing emails over public Wi-Fi.
E2EE ensures that only the intended recipient can decrypt your emails. Messages on Mailfence are encrypted on the sender’s device and decrypted only on the recipient’s device, preventing anyone else (including service providers) from accessing their contents
Logging out ensures that your email account remains inaccessible to unauthorized users, especially on shared or public devices. Even on personal devices, logging out adds an extra layer of security if your device is lost or stolen.



