Spam vs phishing attempts – do you know the difference? Every day, a new data breach or leak is made public. This means that, unfortunately, most of our email addresses are now freely available on the dark web, making them an easy target for spam and phishing attempts.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about spam vs phishing attempts, what sets them apart, and how to avoid falling victim to one of them. Let’s get started!
What is Spam?
Spam email (or “junk mail”, or “spamming”) refers to unsolicited emails.
These messages are mostly promotional and aimed at pushing products or services.
Spam emails can range from a simple nuisance to actually compromising your security. Indeed, they can sometimes contain harmful links or malware (which might make them a phishing attempt, but more on that later).
It’s important to note that spam email is a subjective notion. What some people consider “spam” may not be spam for somebody else. Technically, spam email refers to unsolicited emails. However, the term has taken on a broader meaning in recent years. Let’s look at an example:
In this example, I signed up for a popular newsletter by Tim Ferris. However, after some time, I stopped reading the emails I received. I might now consider this sender “spam” even though I initially signed up for his emails.
Likewise, when you order a product on a new website, you might (unknowingly) agree to receive their marketing emails, newsletter, product news, etc. In this case, although you technically signed up for those emails, you might quickly consider them as spam.
Spam email example
Finally, there is the case of truly unsolicited emails.
This happens when your data is leaked or shared with advertisers. You then start receiving emails from senders you’ve never heard of. In 99% of cases, these emails want to sell you something. Or they might ask you for some sort of collaboration.

The bottom line? Spam emails can be irritating, but they should not be confused with actual scams or phishing attempts. This is what we are going to explore in the next section.
Check out this guide to learn more about how Mailfence handles spam emails.
What is Phishing?
Phishing is a type of attack designed to trick individuals into sharing personal data such as:
- passwords;
- financial details
- or other confidential information.
The term phishing comes from the word “fishing:” Attackers are luring people into traps, similar to how fish are caught with bait.
The use of “ph” instead of “f” likely originated from hacker culture, where alternative spellings were common.
Phishing attacks often appear to come from trustworthy sources, such as banks or popular online services but are actually crafted by cybercriminals to steal your information. Phishing attacks rely on creating urgency or panic to manipulate victims into clicking harmful links or sharing sensitive data.
We have a comprehensive guide on how to spot email phishing attacks, but here’s what you should know:
- an attacker sends a massive amount of emails to random people. These messages are all identical and contain a link pointing toward a spoofed website to induce the reader to leave his credentials;
- a phishing attack often includes threats that an account of yours will be closed if don’t take action. Or they might tell you that your security has been compromised in some way;
- in case you receive a message from a trusted organization, double-check the sender’s email address. The attacker might be using a very subtle variation based on the organization’s legitimate email address.
Modern phishing schemes are increasingly sophisticated, mimicking the appearance of legitimate communications to an unsettling degree. That’s why it’s crucial to double-check any links before you click on them (but more on that later).
Key Differences Between Spam and Phishing
Although spam and phishing can look similar, they are distinct in several important ways.
In terms of objectives, spam emails are designed for advertising purposes. They are often unsophisticated and try to reach as many people as possible without specific targeting.
On the other hand, phishing is a far more targeted and malicious form of attack. For example, the famous Ledger data breach exposed the email addresses of thousands of cryptocurrency holders. These people were then targeted with various phishing attacks centered around cryptocurrency. Here’s an example:

As you can see, this type of attack can be very refined in terms of its layout and who it targets. Phishing attacks often mimic legitimate communications, copying the branding and communication style of a trusted sender.
In some cases, phishing attacks can be hyper-targeted on a specific individual. In this case, they are called spear phishing attacks.
Tackling Spam vs Phishing
The way you tackle spam vs phishing attacks is quite different. Here’s what you can do in both cases.
To protect yourself from spam, activate spam filters on your email service.
This is the most effective way to filter out unwanted emails. In Mailfence, our strong antispam filters are enabled by default when you create your account. If you notice a spam email that has reached your inbox, you can mark it as spam by right-clicking on it > Mark > Spam. In some cases, our antispam filter might flag something that is not actually spam, in which case you will need to whitelist the sender.
When it comes to phishing, always verify the sender’s email address carefully.
If there is any sense of threat or urgency in the email, assume it’s a phishing attack. Phishing emails often use addresses that closely resemble legitimate ones, with only slight variations. If you’re not sure, cross-check the address with an email you know for sure is legitimate.
If you’re still unsure, contact customer service through their official contact form, support email address, or phone number. In any case, you should NEVER click on a link or button without being 100% sure the sender is legitimate.
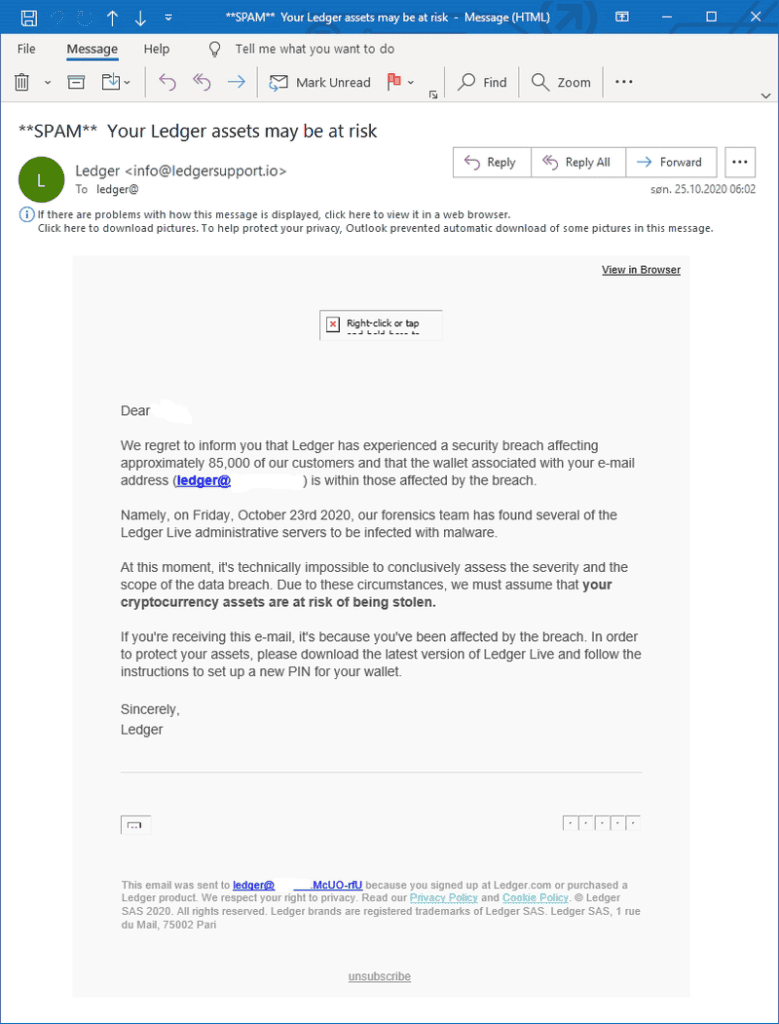
In the above example, the email is coming from the domain “ledgersupport.io,” a domain created just one day prior and not linked in any way with Ledger.
Additionally, using two-factor authentication on your accounts adds an extra layer of security. In case attackers get access to your login credentials, they still won’t be able to enter your account.
That’s it for this Guide on Spam vs Phishing!
That’s a wrap for this guide on spam vs phishing! While both spam and phishing are forms of unwanted communication, they differ greatly in intent and impact. We hope this guide helped you understand the difference between the two and will prevent you from becoming a victim in the future!
Staying safe online starts with a private and secure email. Here at Mailfence, we pride ourselves on being one of the most private and secure emails. Not only that, but your free account also comes with online storage for your most important documents, a calendar, contact management, and much more. Create your free account today, no strings attached:
Got any questions? Feel free to check out our Knowledge Base, or drop us a line at support@mailfence.com.
FAQs: Spam vs Phishing
Spam refers to unsolicited, often promotional emails, while phishing involves targeted attacks designed to steal sensitive information like passwords or financial details. Phishing emails mimic legitimate sources and create urgency to deceive victims.
To avoid spam, use email services with strong spam filters, like Mailfence, which automatically filter out unwanted emails. If spam reaches your inbox, mark it as spam to improve filtering accuracy. Avoid sharing your email address publicly to reduce exposure
Phishing emails often create urgency or panic, use slight variations of legitimate email addresses, and include links to spoofed websites. Always verify the sender’s email address and avoid clicking on suspicious links. When in doubt, contact the organization through official channels.
Mailfence provides robust antispam filters enabled by default and supports two-factor authentication for added security. This ensures a private and secure email experience, helping users stay safe from spam and phishing attacks.




