If you’ve spent any time online, then you have surely come across an OTP or one time password.
However, you might be confused as to what they are exactly. When should you use them? And what’s the difference between OTP, 2FA, MFA, and other similar terms?
In this article, we will cover everything you need to know about one time passwords, and why they are one of the best ways to secure your online life. Let’s get started.
What is an OTP in a Nutshell?
A one time password generates a temporary code for identity verification. You can be asked to enter such a code during a login or before an important transaction.
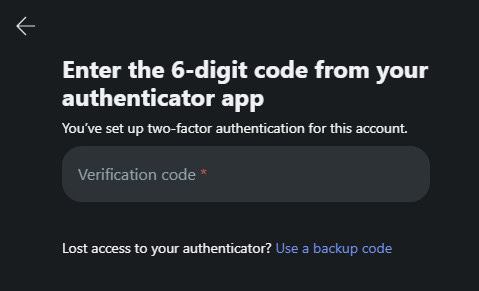
Unlike traditional passwords, which remain static, OTPs change with every use, which is why they are called “one time”.
Their primary function is to secure your accounts. Even if your primary password is compromised, without the one time password, a hacker will not be able to enter your account. OTPs are generally received via SMS, email, an authenticator app, or a dedicated device.
Different Types of OTP
When you decide to enable 2FA on an account, you will see that multiple methods are available. Here are the most popular ones.
SMS-based OTP
This method delivers a one-time password straight to your mobile device via SMS.
It’s the most common approach and offers quick access without the need for additional apps.
However, we discourage you from using this method. Although convenient, SMS-based OTPs are vulnerable to risks like SIM swapping. We explore this more in detail in the section on the downsides of OTPs.
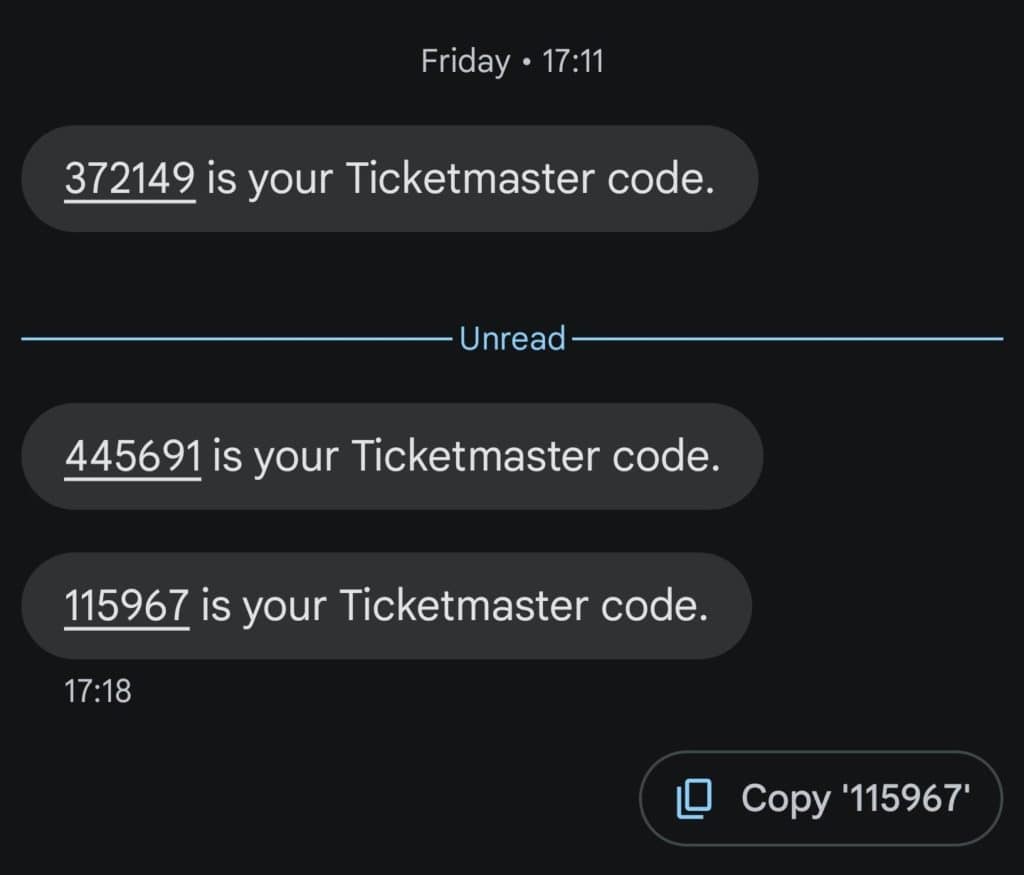
App-based OTP
Authenticator apps, such as Authy, generate OTPs directly on your phone.
These codes refresh every 30 seconds and are linked to your device, making this method much more secure than the SMS-based one.
There are a multitude of different authentication apps out there, each with its tradeoffs. You can check this website for a comprehensive list of authentication apps. The only recommendation we have is to avoid using Google services, including Google Authenticator 😊.
App-based OTPs are not vulnerable to SIM swapping, and they function even when your device is offline.
Device-based OTP
Also known as hardware tokens, device-based OTPs involve a small physical device (like a USB key).
This method offers the highest level of security since it operates offline and is immune to phishing attacks.
However, the inconvenience of carrying a separate device and the risk of losing it are notable drawbacks. If you misplace your hardware token, regaining access to your account can be challenging.

How Can I Activate a One-Time Password on My Accounts?
Although OTPs might sound technical, they are actually quite simple to set up. But before going through how to activate an OTP on your accounts, let’s clarify a few terms:
- OTP stands for “one time password”, an additional code that you need to enter after your primary password. You might also see terms like HOTP or TOTP, which are simply different types of OTPs but serve the same function;
- 2FA stands for “2-factor-authentication”. This describes the broader process of having two separate steps to connect to your account (your primary password + an OTP);
- MFA stand for “multiple-factor authentication”. This includes 2FA, but extends to methods of authentication that include more than two steps.
To enable OTPs, you’ll need to go into the security settings of each account and choose two-factor authentication (2FA). Be aware that although most services offer 2FA, not all do. 2FA is a crucial aspect of securing your accounts, so you should avoid services that do not offer it.
Here are the steps you can follow to activate 2FA on your Facebook account:
- Log in to your Facebook account.
- Go to Settings & privacy > Settings.
- Click on Security and Login.
- Under Two-Factor Authentication, click Edit.
- Choose your preferred OTP method (e.g., SMS, app-based).
- Follow the on-screen instructions to finish the setup.
If you have multiple Meta accounts, you might need to go to the Accounts Center > Account Settings > Password and Security. Then select and activate “Two-factor authentication”.
Once activated, you can choose to “Trust this device”. This means you will not need to re-enter your OTP every time you log in on that device. However, we do not recommend this, as it undoes the additional security provided by 2FA.
X (formerly Twitter)
For X:
- Open the app and go to More > Settings and privacy.
- Tap on Security and account access > Security.
- Select Two-Factor Authentication.
- Choose between SMS, an authentication app, or a security key.
- Follow the prompts to activate OTP for your account.
For Reddit:
- Sign in to your Reddit account.
- Navigate to User Settings.
- Click on Privacy & Security.
- Under Two-Factor Authentication, click Enable.
- Choose your preferred method to receive OTPs.
- Complete the setup by following the instructions.
For LinkedIn:
- Go to your LinkedIn homepage and click on Me at the top.
- Select Settings & Privacy from the dropdown.
- Under Account, click Login and security.
- Find Two-step verification and click Set up.
- Choose your OTP method and follow the on-screen steps to activate it.
Google Accounts (Gmail, YouTube, etc.)
- Sign in to your Google account and go to Security.
- Under Signing in to Google, select 2-Step Verification.
- Click Get Started and follow the instructions.
- Choose how you want to receive OTPs (e.g., Google Authenticator, SMS).
- Complete the setup.
Mailfence
As one of the most private and secure email providers, Mailfence also offers 2FA:
- Log in to your Mailfence account.
- Go to Settings > Account > Security.
- Click on Two-Factor Authentication and select Enable.
- Choose your preferred OTP method.
- Follow the steps to complete the setup.
Looking to create an email account with no phone number required? Check out our latest guide here.
Should I Activate OTP on All My Accounts?
If you’ve made it this far in this guide, then you likely want to improve your online security.
If so, then yes, setting up OTP on all your accounts is a solid strategy for improving your cybersecurity.
Although the activation process may seem repetitive, the security benefits far outweigh these minor inconveniences. Whether it’s for social media or banking services, OTPs substantially reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
It may seem like a daunting task to activate 2FA on all your accounts at once. This is why we recommend taking it step by step. Email should be the first account where you activate an OTP. This is because an attacker with access to your email account could reset passwords to other accounts, leading to a chain reaction of breaches. Once that is done, take on accounts that store sensitive information. This includes accounts that you use on a daily basis: financial data, cloud storage and social media.

Even if an account doesn’t hold critical information, losing control of it can still lead to severe consequences. Data breaches have shown that attackers often target weaker platforms to gain access to more valuable ones. OTPs are an essential step to secure the perimeter of your online identity.
Is a One-Time Password Truly Safe?
While OTPs are a powerful security measure, it’s important to realize that no method is completely foolproof. OTPs significantly strengthen your defenses against basic password theft, but are not a silver bullet.
SMS-based OTPs are particularly susceptible to security threats like SIM swapping. This is where attackers hijack your phone number to receive the OTP.
That is why we do not recommend you use this method and opt for a more secure one like a dedicated app or device.
App-based OTPs are much safer since the codes are generated locally on your device and do not travel over the network. However, it’s still essential to protect your phone or device with a strong PIN or biometric security, as an unlocked device could still be compromised.
Despite these potential risks, OTPs remain one of the best options for enhancing security. When combined with strong, unique passwords and caution against phishing attacks, they create a formidable defense against most cyberattacks.
What Are the Downsides of Using an OTP?
While OTPs are an effective method to protect your accounts, they come with some downsides. Here are a few potential issues to consider.
Convenience
OTPs add an extra step to your login process. While it may only take a few seconds to enter a code, this can feel like a burden for users who log in frequently or manage multiple accounts. For some, the convenience of password-only access might seem preferable, though this greatly reduces security.

Device Dependency
If you rely on app-based or SMS-based OTPs, losing your phone can create significant problems. If your phone is stolen, broken, or simply misplaced, you might find yourself locked out of multiple accounts. While most platforms offer backup codes or recovery options, the process of regaining access can be time-consuming and frustrating.
Vulnerabilities
As discussed, OTPs aren’t immune to threats. SMS-based OTPs can be intercepted via SIM-swapping. Even app-based OTPs, while much safer, could still be compromised if malware infects your phone. There could also be a vulnerability when you update the app.
Backup and Recovery
One overlooked aspect of OTPs is the need for backup and recovery plans. If you don’t store recovery codes in a secure place, you could be permanently locked out of your accounts if you lose access to your OTP method. Some services offer alternative methods to regain access, but this process often requires proof of identity and can take time.
System Compatibility
Not all services offer OTP or multi-factor authentication, which could leave some accounts less protected. Additionally, some platforms only support certain OTP methods, which might require you to manage multiple OTP setups
That’s it for this Guide on What is an OTP!
That’s a wrap for this article! Hopefully, you now have a better understanding of what an OTP is, and the broader concept of 2FA.
If you’re conscious about your online privacy and security, make sure to create your free Mailfence account today, which includes:
- end-to-end encrypted emails;
- secure online storage;
- secure Calendar;
- a contacts management tool;
- … and a lot more!
Any questions? Feel free to check out our Knowledge Base, or drop us a line at support@mailfence.com
What is a One-Time-Password? FAQ
An OTP (One-Time Password) is a temporary code used for identity verification during logins or transactions. It changes with every use, providing an additional layer of security to protect accounts, even if the primary password is compromised
OTPs can be received via SMS, authenticator apps, or hardware devices. SMS-based OTPs are convenient but vulnerable to SIM-swapping attacks. App-based OTPs are more secure since they generate codes locally on your device. Hardware devices, like YubiKey, provide the highest level of security but can be less convenient.
Yes, enabling OTPs across all your accounts significantly enhances your online security. Start with critical accounts like email and financial services, then expand to other accounts. OTPs minimize the risk of unauthorized access, even if passwords are compromised.
While OTPs strengthen account security, they are not foolproof. SMS-based OTPs can be intercepted, and device-based methods depend on the security of the device. Combining OTPs with strong passwords and vigilance against phishing attacks offers the best protection.