In this blog post, we explain the major differences between symmetric vs asymmetric encryption. This article will also explain which encryption method you should use.
Sign up to the Mailfence Newsletter!
Stay up-to-date with the latest news in the world of online privacy and cybersecurity
Some words about different encryption methods
In today’s world, scammers and other cybercriminals are becoming increasingly present, affecting millions of users. To prevent these individuals from stealing our data, we have to encrypt everything. Luckily, there are three different encryption methods that you can use: symmetric encryption, asymmetric encryption, and hash functions (Keyless).
Right now, we’ll focus on symmetric encryption vs asymmetric encryption and leave the third (hash functions) for a later time.
Mailfence uses symmetric and asymmetric encryption, as each method has pros and cons. You will learn more about that later. Both encryption methods use keys to encrypt and decrypt data. The main difference is that symmetric encryption uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt data. In contrast, asymmetric encryption uses a pair of keys – a public key to encrypt data and a private key to decrypt information.
| Symmetric Encryption | Asymmetric Encryption |
| Uses a single key to encrypt and decrypt data | Uses a public key to encrypt data and a private key to decrypt data |
| Faster encryption process | Slower encryption process |
| Example key sizes are 128 or 256-bit long | Example key sizes are 2048-bit or longer |
| Doesn’t use a lot of resources | Uses more resources |
| Cipher text is smaller, or the same size as the original plain text | Cipher text is larger or the same size as the original cipher text |
| Both symmetric and asymmetric algorithms provide authentication capability | Both symmetric and asymmetric algorithms provide authentication capability. Only non-repudiation can be achieved using an asymmetric algorithm. |
| Example algorithms are AES, DES, 3DES, IDEA and Blowfish | Example algorithms are RSA, ECC, DSA and El Gamal algorithms |
| Better at handling and transferring large amounts of data | Better at handling and transferring smaller amounts of data |
| Has the risk of someone stealing the key if it is not managed properly | Has the risk of losing the private key (the keypair is irrevocable |
What is symmetric encryption?
Symmetric encryption, aka symmetric key cryptography, uses one single key to encrypt and decrypt data. You have to share this key with the recipient. Let’s say you want to sent “I love you Mom”. You would write your email, then set a secret key, or password, to encrypt it. Then, you would simply send it. When mom receives the message, she would enter the same secret key to decrypt the email.
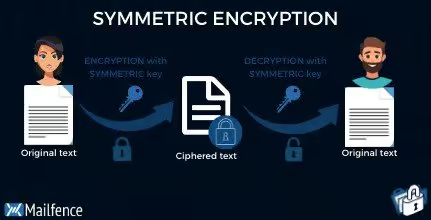
Pros and cons of symmetric encryption
Let’s take a look at some of the pros and cons of symmetric encryption:
Pros:
- Easier to implement and use
- Faster than asymmetric encryption
- Less resource-intensive
- Good for handling and transferring larger amounts of data
Cons:
- Loss of a key will mean that data encrypted with it is compromised
- Key has to be shared securely with the other party
How does Mailfence incorporate symmetric key cryptography?
Mailfence offers password-encrypted messages (PEM) based on symmetric encryption. Our solution allows you to set a password hint that helps the recipient decrypt the message. You can share your passphrase via SMS, a phone call, or during a physical meeting.
Also, with Mailfence’s PEM, you can set an expiration date for the email. After the expiration date, the email cannot be decrypted any more. Furthermore, we store password-encrypted messages in a zero-knowledge environment and encrypt them with your password. That way, only you and the intended recipient can access the message.
In case you would like to know more, visit our dedicated knowledge base.
Here are some good practices to follow for our PEM:
- Never use your OpenPGP passphrase
- Never use your Mailfence account password
- If you are sending a sensitive message, make sure unwanted readers cannot guess your password
There are many symmetric encryption algorithms, such as AES, DES, 3DES, IDEA. For your information, Mailfence uses AES in combination with other ciphers.
What is asymmetric encryption?
As stated earlier, public-key encryption requires two keys to work. Firstly, a public key must be made public to encrypt the data. Also, a private key is used to decrypt the data. It sounds complicated enough, but we made it easy to use. Let me break it down. Basically, it would be like sharing lockers with anyone wanting to contact you, whereas you’re the only one with access to the key.
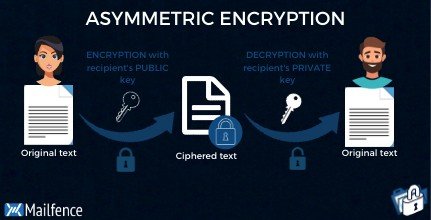
The public key and the private key are not the same thing, but they are related. You write your message, then encrypt it with the recipient’s public key. After that, if the recipient wants to decrypt your message, they would have to do it with their private key. Keep the private key private at all times. The best practice would be to store it locally. One requires greater knowledge than the average person to make this happen.
The emailing software of the recipient will see if the private key corresponds with the public key, and then it will prompt the user to type the passphrase to decrypt the message.
Some best practices for asymmetric encryption:
- Use 2048-bit or longer keys
- Store your private key locally, so you don’t forget it
- Don’t share your private key with anyone
Creating strong keys is the foundation of asymmetric encryption. A good encryption practice would be to use multiple encryption methods instead of just one. Not everyone knows how to use public-key encryption, so there may be occasions you have to use different encryption methods.
Mailfence uses asymmetric encryption based on the RSA-algorithm for OpenPGP-based keys. ECC (Curve 25519) algorithm for OpenPGP-based keys is also supported.
Pros and cons of asymmetric encryption
Asymmetric encryption also has its advantages and disadvantages. Let’s take a look at what they are:
Pros:
- Data can only be decrypted using the private key held by the owner
- If the public key is lost or stolen, data won’t be compromised
- Provides authentication and non-repudiation in addition to confidentiality
Cons:
- It’s slower than symmetric encryption
- Uses more resources
- If the private key is lost, there is no way to retrieve it
Thoughts on symmetric vs asymmetric encryption
Which encryption should you use? Use symmetric encryption when you would like to send a quick encrypted message. Use asymmetric encryption when you have your recipient’s verified OpenPGP public key. Combine public-key encryption with digital signatures if you don’t want to take any chances. Don’t know how to send encrypted emails? Find out more in our blog post.
Symmetric vs asymmetric encryption was a very important article for us to write. We hope we have clarified the concept of symmetric vs asymmetric encryption. Stay tuned because Mailfence is planning to release more of these educational articles soon.
FAQ section
Symmetric encryption uses a private key to encrypt and decrypt an encrypted email.
Asymmetric encryption uses the public key of the recipient to encrypt the message. Then, if the recipient wants to decrypt the message, the recipient will have to use their private key to decrypt. If the keys correspond, then the message is decrypted.
In our opinion, one encryption method is not better than the other. It’s just a different way of encrypting. The user has to be mindful if they follow the best security practices at all times.
The biggest disadvantage is that you have to share the secret key somehow. There are many ways to share it. However, if an attacker finds out what the secret key is. Then emails that were encrypted with that secret key are compromised.


