If you’ve found your way to this article, you are likely asking yourself one of these two questions:
- What is a keylogger?
- How do I know if my computer is infected by a keylogger?
Luckily, we’ve got all the answers you are looking for and more! In this article, we will cover what keylogger and keystroke logging are, the different types of keyloggers, how to detect if your computer is infected, and our 5 best tips to futureproof yourself against keyloggers.
Note: if you’ve found this article because you are actually looking for a keylogger solution, then keep browsing. Mailfence is not for you 😉
What is a Keylogger?
Let’s start at the top with a defintion of what a keylogger is.
A keylogger is a piece of software or hardware that can intercept and record the input from the keyboard of a compromised machine.
In some cases, this can be done with the user’s consent (more on that later). However, in most cases, a keylogger works without the user’s knowledge. The keylogger can then either store the recorded data locally or send it to a remote PC controlled by the attacker.

This means that the person controlling the keylogger can know virtually everything you do online. Think about it: what have you typed today on your keyboard? Probably several passwords, websites you’ve visited, messages and emails, maybe even credit card numbers.
This means a keylogger is one of the most dangerous pieces of malware you can come across.
What is a keystroke?
So far, we’ve defined a keylogger as a device or software that can record keystrokes. But what exactly are keystrokes?
A keystroke is any time you press on a key of your keyboard.
It is how you interact with your computer (in addition to the clicks and movements of your mouse). So when a keylogger records every single keystroke, it’s as if somebody was listening to your conversations. Except these conversations are some of the most private ones you will have!
But before diving into the dangers of keyloggers, let’s examine a few legitimate use cases.
Legal uses of keystroke logging
Installing a keylogger is not always a criminal act. There exist very legitimate uses for keystroke logging:
- Employee Monitoring. Although this might sound invasive to some, companies may use keyloggers to monitor employees. In particular, they will monitor computer usage to maintain productivity and adherence to company policies. This can help prevent data leaks, insider trading, and more. As long as this policy is clearly stated in the employee’s contract, this is a legal use of keyloggers.
- Parental Control. While not every parent may agree with this approach, some will use keyloggers to oversee their children’s online activities. This can help protect them from inappropriate content and online predators.
- Law Enforcement. Law enforcement agencies may use keyloggers during investigations to gather evidence and track criminal activity. In these cases, the use of keyloggers is typically regulated and requires proper authorization.

In these scenarios, the use of keyloggers must be balanced with privacy considerations and comply with legal regulations. As a general rule of thumb, the individual or entity installing the keylogger also needs to be the owner of the computer on which it is installed. Further legal considerations may differ from country to country.
Different Types of Keyloggers
Now that we’ve covered what a keylogger is, let’s cover the different types.
Keyloggers can be broadly categorized into two buckets: hardware vs. software.
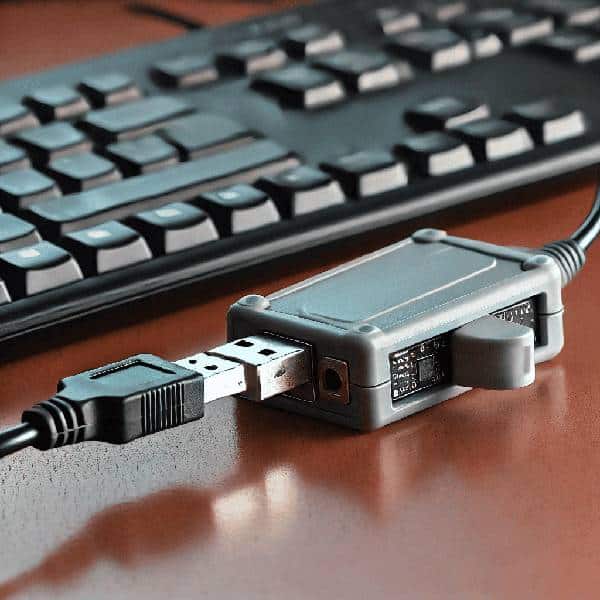
Hardware keyloggers
Hardware keyloggers are physical devices connected to a computer. They are less common and more difficult to implement. Implementation can be done either during the manufacturing process or after deployment. Some hardware variants can be installed during the manufacturing process, including BIOS-level keyloggers.
They can be placed between the keyboard and the computer, intercepting the keystrokes as they are transmitted. There are different types of hardware keyloggers, including:
- USB Keyloggers: These devices are plugged into the USB port of a computer, with the keyboard connected to the keylogger. They can capture all keystrokes typed on the keyboard. Alternatively, they can be integrated directly into your keyboard.
- Wireless Keyloggers: These devices intercept signals from wireless keyboards, capturing the keystrokes transmitted over the wireless connection.
In the case of wireless keyloggers, they can often be difficult to detect. This is because they do not rely on software and can operate independently of the computer’s operating system. This means no antivirus will be able to pick them up.
Software Keyloggers
These are often installed as part of a larger piece of malware, such as a Trojan or rootkit. Such a keylogger is easier to get onto a target machine since it typically doesn’t require physical access. It has the ability to impersonate an API on the target machine’s operating system, which allows the keylogger to record each keystroke as it’s made. There are several variants of software keyloggers:

- Kernel-Level Keyloggers: These keyloggers operate at the kernel level, which is the core of the operating system. They can intercept keystrokes directly from the keyboard driver, making them very difficult to detect and remove.
- API-Based Keyloggers: These keyloggers use the application programming interfaces (APIs) provided by the operating system to capture keystrokes. They are easier to detect than kernel-level keyloggers but can still be effective.
- Form Grabbing Keyloggers: These keyloggers capture data submitted in web forms, such as login credentials and credit card information. For example, a fake website pretending to be your bank can record what you type in the “username” and “password” sections.
- Screen Scrapers: Although not traditional keyloggers, screen scrapers capture the screen content rather than keystrokes. They can be used to capture information entered through virtual keyboards or on-screen keyboards. Tell signs will be your screen going dark for a fraction of a second at regular intervals, i.e. a screenshot was just made.
Software keyloggers are more common than hardware keyloggers because they can be distributed and installed remotely, often without the user’s knowledge.
Is My Computer Infected?
Detecting a keylogger on your computer can be challenging, as they are designed to operate covertly. There often won’t be any obvious signs such as with most social engineering attacks. However, look out for the following alerts that may inform you of a keylogger infection:
- Slow Performance: If your computer suddenly starts running slower than usual, it could be due to a keylogger running in the background.
- Unusual Activity: Look for unexpected pop-ups, changes in your browser settings, or unfamiliar programs running on your computer. These could be signs of malware, including keyloggers.
- Increased Network Activity: Keyloggers may transmit captured data to a remote server. If you notice unusual spikes in network activity, it could be an indication of a keylogger.
- Antivirus Alerts: Regularly update and run your antivirus software. Many antivirus programs can detect and remove keyloggers and other types of malware.
- Task Manager: Check your task manager for unfamiliar processes. Some keyloggers may show up as running processes under names that may not be easily recognizable.
I’m sure there’s a keylogger on my computer… What next?
If you suspect that a keylogger has been installed on your computer, don’t panic! Follow these steps to remove it and protect your information:
- Disconnect from the Internet: Immediately disconnect your computer from the Internet to prevent any data from being transmitted to a remote server.
- Run a Full System Scan: Use your antivirus software to perform a full system scan. Make sure your antivirus definitions are up to date.
- Identify and Remove Suspicious Programs: Go through your list of installed programs and look for any that seem unfamiliar or suspicious. Uninstall these programs. If you’re unsure about a program, search for it online to check it’s purpose.
- Change Your Passwords: After removing the keylogger, change all your passwords, especially for sensitive accounts like email, banking, and social media. You can also ask your bank to block your credit cards and issue new ones.
- Monitor Your Accounts: Keep an eye on your financial and online accounts for any unusual activity. Let your colleagues, family, and friends know that you were the victim of a keylogger and pay extra caution to any communication coming from your accounts.
- Use Anti-Keylogger Software: Consider installing specialized anti-keylogger software to provide an additional layer of protection against future attacks. Also, consider changing or updating your antivirus software.
What About my Smartphone?
So far, we’ve covered keyloggers exclusively in the context of your computer. But what about your smartphone? Should you be worried about a keylogger installed there too?

Smartphones are not immune to keyloggers. In fact, mobile devices can be even more vulnerable due to the wide range of apps and permissions that users grant.
Here are some ways to determine if your smartphone is infected:
- Battery Drain: If your battery life has significantly decreased, it could be due to a keylogger or other malware running in the background.
- Data Usage: Monitor your data usage for any unusual spikes. Keyloggers may use your data to transmit captured information.
- App Permissions: Review the permissions granted to your installed apps. Malicious apps may request excessive permissions to access your keystrokes and other sensitive information.
- Unfamiliar Apps: Look for any apps you do not remember installing. These could be disguised keyloggers or other types of malware.
- Performance Issues: Just like with computers, a slow or lagging smartphone could be a sign of malware.
To protect your smartphone, only download apps from trusted sources, keep your operating system updated and use a reputable mobile security app to scan for malware.
6 Tips to Prevent Getting Infected by a Keylogger
Social engineering techniques are becoming more and more sophisticated. That’s why it’s crucial to always stay alert and suspicious when online.
To protect your devices from any keyloggers, follow these 5 tips:
- Do not download any pirated and other suspicious freeware software.
- Maintain a password-change schedule (for e.g. every 3 weeks).
- Use ‘Limited privileges’ based OS profile, for daily low-profile tasks. This is a profile that does not have admin access.
- Use a modern and up-to-date browser (for e.g. Firefox, Brave…), that will help you in avoiding Man-in-the-browser (MitB) attacks.
- Back-up your data, to avoid data loss in case of account compromises.
- Use 2-factor authentication on your accounts, as it will protect your account even if your password gets compromised
Last Words on Keylogger Protection
That’s it for this guide on keyloggers! We hope you found it useful, and will now be able to protect yourself against keyloggers in the future.
A safe Internet means using a safe, secure and private email. That’s why we built Mailfence. Create your free account here.