Knowing how to encrypt a file is such an underrated skill to have.
Not only does encrypting your files protect your sensitive data from cybersecurity breaches. It also protects your right to privacy.
So, in this article, we are going to outline the following:
- What it means to encrypt a file.
- Why file encryption is so important.
- Five different ways you can use to encrypt a file.
If you want to get started today, create your free Mailfence account to start encrypting your emails, files, and more.
To Encrypt a File – What Does it Mean…?
So, what do we mean when we say you need to encrypt your files?
Essentially, to encrypt a file is like putting it in a special, secret box.
This is a box where anything inside it gets totally scrambled. To unscramble the data, you need the right key, which is unique. So unless someone has the key to the box, they won’t be able to access any of the information. Even if they get their hands on the box.
Here’s an example taken from our Mailfence secure inbox:
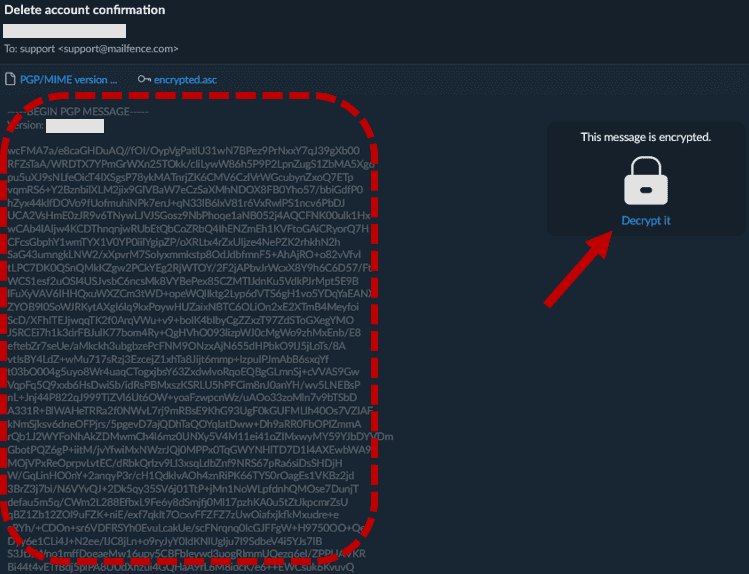
In this example, a customer encrypts an email before sending it. You can see how the content of the email is completely scrambled. To make any sense of it, we need to decrypt the mail. To do this, we need our secret key:
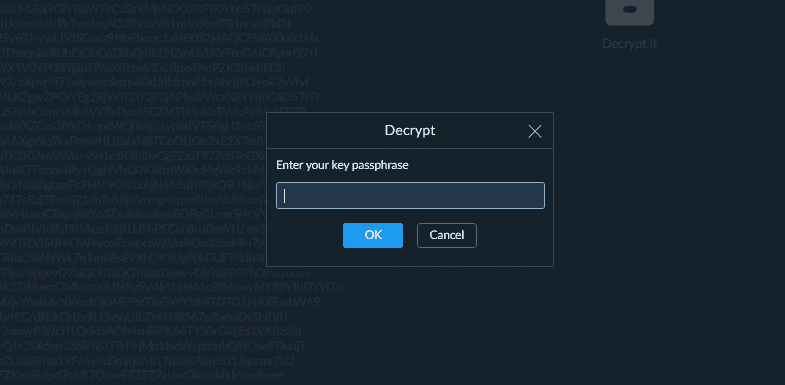
In this particular example, the email was encrypted using PGP. We’ll come back to it later in this article. But if you want to learn more, check out this guide here.
Once a file is encrypted, you can store or send it safely. As long as your secret key remains safe, your files are safe.
What are the Risks When You Don’t Encrypt a File?
Unfortunately, most people don’t encrypt their files.
When this happens, you expose yourself to several different risks:
- Data Breaches. Without encryption, sensitive information becomes vulnerable to unauthorized access. This can lead to data breaches, where hackers can easily steal and misuse your data.
- Identity Theft. A 2022 study estimated that 27 million US citizens were the victims of identity fraud in 2021. With identity theft, personal details can be accessed. These include social security numbers, bank details, logins and passwords,and more.
- Financial Loss. Unencrypted financial data can be exploited by cyber-criminals, resulting in monetary losses through fraudulent transactions or account access.
- Reputation Damage. A breach of confidential information can harm an individual’s or organization’s reputation, eroding trust with customers, clients, or partners.
- Legal Consequences. Non-compliance with data protection laws and regulations like GDPR or HIPAA may lead to legal penalties, fines, or lawsuits.
- Ransomware Attacks. If you don’t encrypt your files first, a hacker might do it for you. This is what happens with ransomware attacks. In such cases, hackers encrypt data on your computer. Then, they demand a ransom for its release.
- Loss of Privacy. Personal and sensitive conversations or files may become accessible to unauthorized individuals, compromising an individual’s privacy. They can also be leaked online and end up in the hands of advertisers.
To avoid these risks, you need to start encrypting your files today!
First off, identify the most sensitive data stored on your computers and hard drives. These could be medical records, bank statements, inheritance documents, passwords, etc. Once you’ve identified the files you want to encrypt, you’re ready to move to the next step.
How to Encrypt a File: 5 Different Methods
Many people think that to encrypt a file, you need to be a computer expert. However, modern tools have made it really easy to encrypt files yourself. And you can do so with minimal technical knowledge.
So here are 5 methods you can try out at home to start encrypting your files.
1. Password-Based Encryption
Password-based encryption is probably the easiest method to encrypt a file. Also known as symmetric encryption, this method uses a single password (or passphrase) to both encrypt and decrypt files. The same key is used for both processes.
Note: a password is a string of characters (“ejkd()$dD12”) while a passphrase is a list of random words (“cat disposal vacation entry because”). More info on passwords vs passphrases here.
Using a password to encrypt a file is simple and user-friendly. And it works incredibly well for individual file encryption. However, this method is vulnerable if the password is weak or compromised.
To encrypt a file on your PC, you can use a tool like 7-Zip:
- Right-click on the file, and then navigate to 7-Zip.
- Select “Add to archive.”
- Enter a strong password.
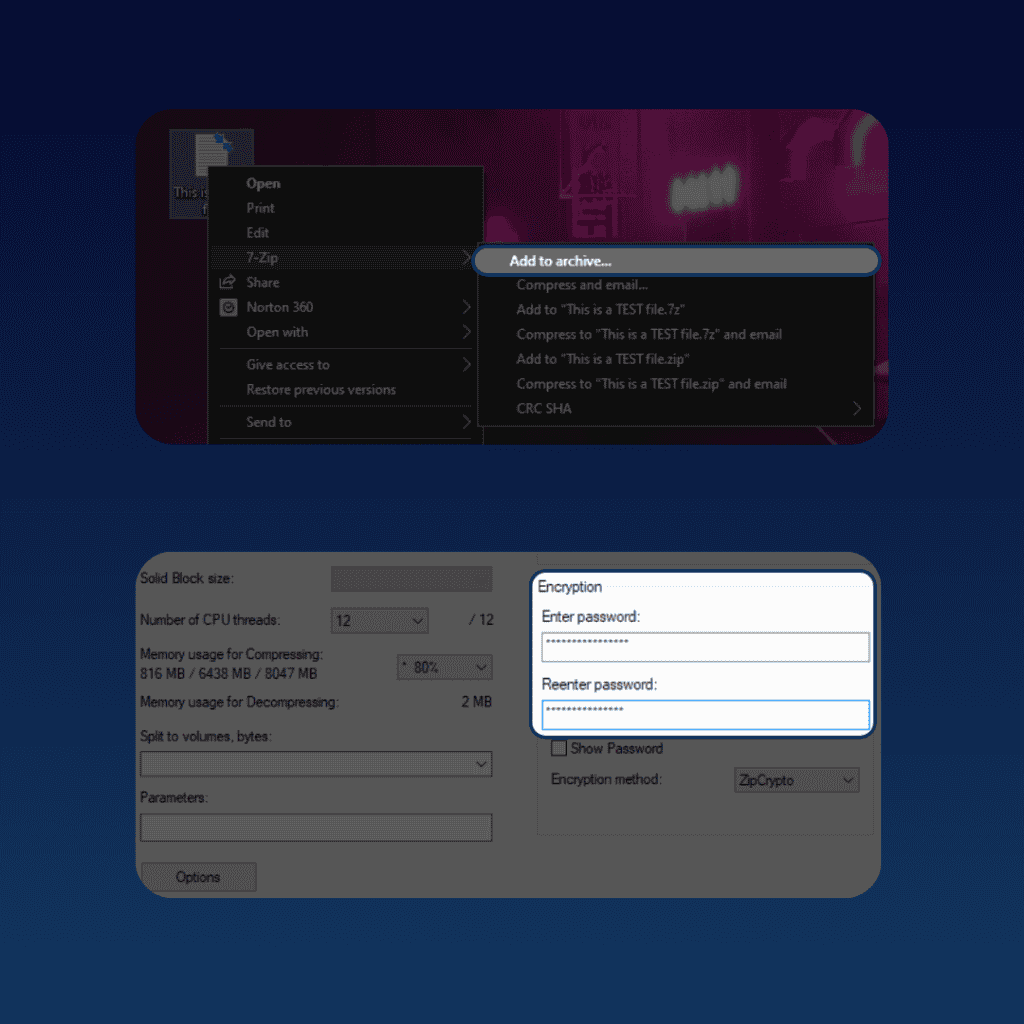
If you’re on Mac, you can use their integrated password-protection.
- For a ‘Notes’ file:
- Right-click on the note you want to encrypt.
- Select ‘Lock Note’.
- Add a password to protect the file.
- Right-click on the note you want to encrypt.
- For other apps:
- Bring up a document in the supported app.
- Choose File > Set Password.
- Add a strong password to protect the file.
- Bring up a document in the supported app.
On Mac, you can also use the famous FileVault encryption method. This will encrypt your entire hard drive. But more on that in section 5.
2. Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
Public Key Infrastructure (or PKI) employs a pair of cryptographic keys. These are known as:
- the public key (for encryption);
- the private key (for decryption).
Users share their public keys while keeping their private keys confidential. If you want to learn more about public key cryptography, check out our full guide here.
Using PKI is highly secure and suitable for secure communication, digital signatures, and authentication. This makes it ideal for secure email and collaborative work.
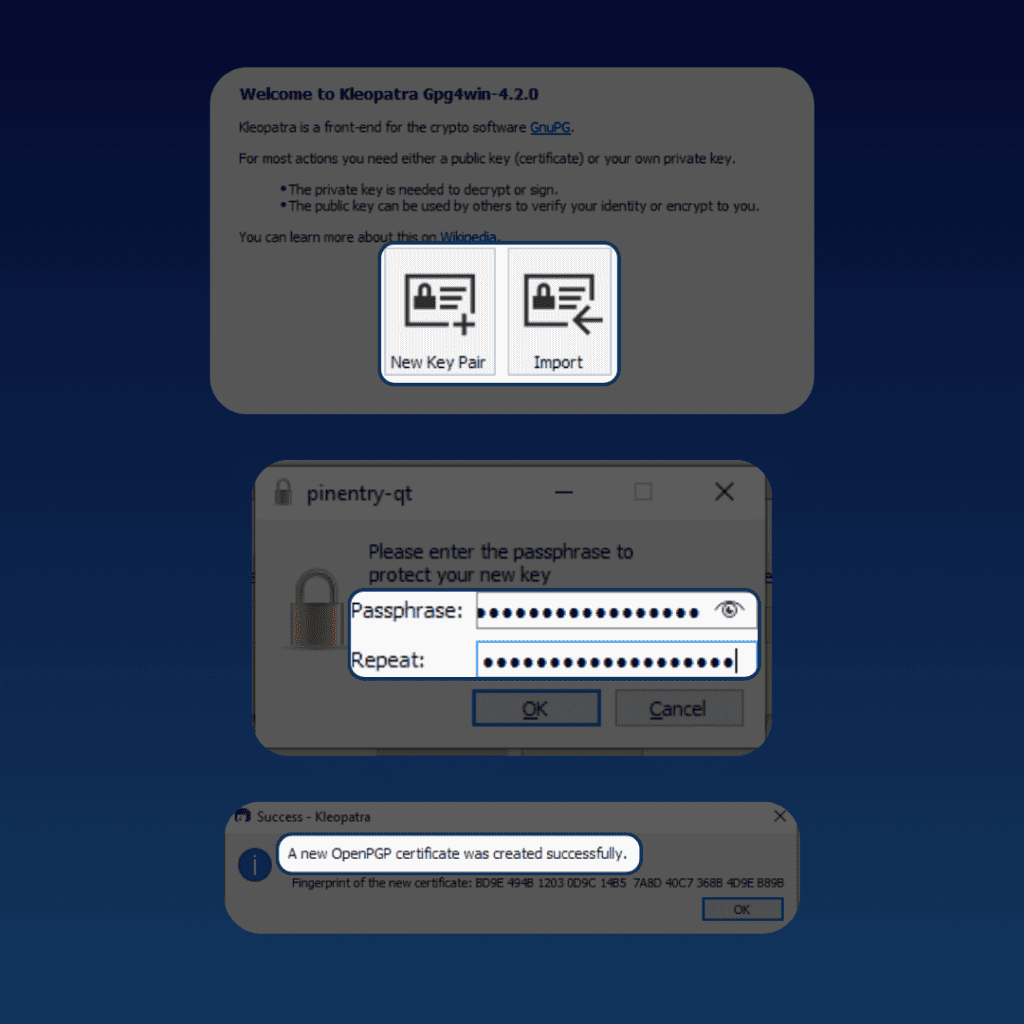
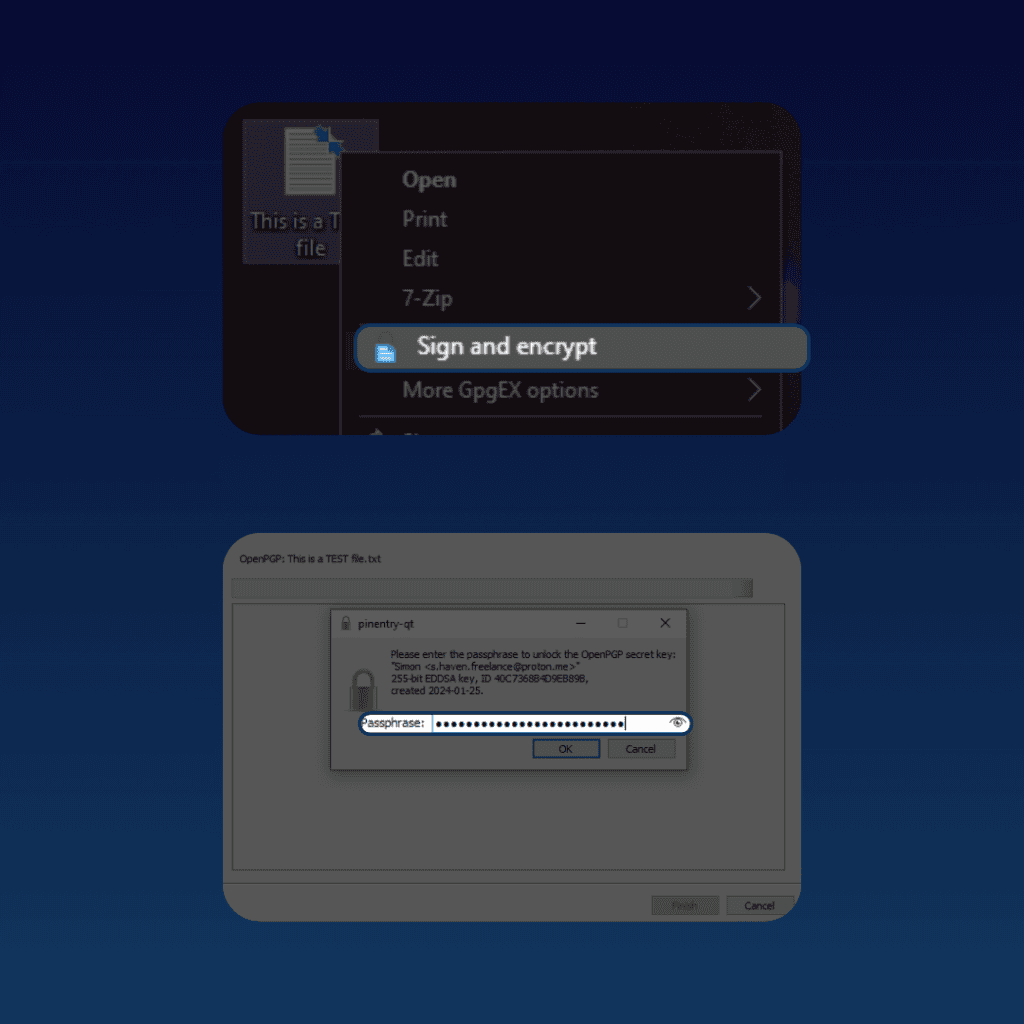
If you’re on Windows, you can use a tool like Gpg4win:
- Download Gpg4win and install it.
- Create an OpenPGP keypair. If you already have one, you can simply import it.
- Right-click on the file you want to encrypt and select “Sign and Encrypt” with the Gpg4win logo.
- Select if you are encrypting files for yourself or others, then click on “Sign / Encrypt”.
- Enter your passphrase.
Did you know that Mailfence allows you to manage your keypairs? Indeed, Mailfence uses OpenPGP encryption to protect your emails without hassle. Every account has an integrated OpenPGP keystore to give you full control over your keys!
If you’re on Mac, you can download GPG Suite and follow a very similar process.
3. Hardware Encryption
Hardware encryption relies on dedicated cryptographic processors within devices.
These can be dedicated USB drives or hard disks. They will automatically encrypt and decrypt data as it’s written and read.
A major advantage of this method is its transparency to the user. It offers robust security and is ideal for portable storage. However, this method can be costly compared to software-based alternatives.
There are hundreds of options on the market when it comes to hardware. Just type in “best hardware encryption” in DuckDuckGo (not Google 😉).
Here are two options that come up in several reviews:
- Samsung T7 Touch SSD: An external SSD that offers hardware encryption with fingerprint authentication for added security.

- Apricorn Aegis Secure Key 3z: A USB drive with hardware encryption and PIN protection.

4. Cloud Storage Encryption
Encrypting a file through cloud storage is another practical method you can use. Cloud storage providers typically offer encryption at rest and in transit. Data is encrypted before uploading and decrypted when accessed.
The main advantages of cloud storage encryption are convenience and availability. However, the security relies on the cloud service provider’s security measures. Users must trust the provider’s encryption practices.
Popular cloud storage tools such as Dropbox and OneDrive offer built-in encryption. This means that all files stored on your Dropbox account are encrypted by default.
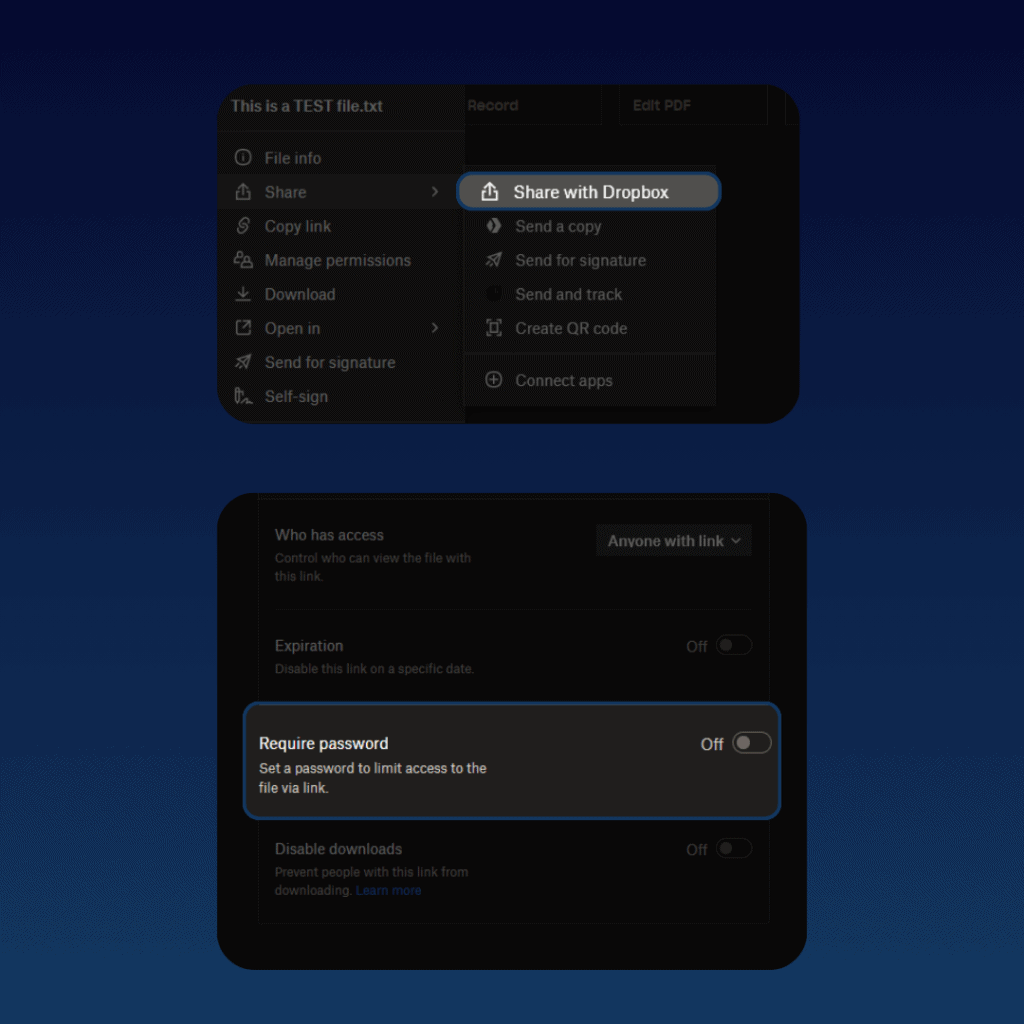
If you have Dropbox Professional, you can add a layer of security when sending files:
- Righ-click on the file you want to send.
- Select Share with Dropbox.
- Click on Settings.
- Enable “Require Password”, and enter a strong password.
5. Full Disk Encryption (FDE)
Finally, one last option consists of encrypting your entire drive.
FDE encrypts an entire storage device, such as a computer’s hard drive or smartphone storage. This renders all data unreadable without the encryption key.
The main advantage is the comprehensive protection for all data on the device. It is also transparent to the user once set up. However, it may slightly impact system performance. And if the device is compromised while unlocked, data is accessible.
To encrypt your computer hard drive on Windows, you can use BitLocker. However, not all PCs will have BitLocker available. If that’s the case for you, you can check out VeraCrypt. This is a free open-source disk encryption software for Windows, Mac OSX, and Linux.
On Mac, you can use FileVault:
- Go to your Apple menu > System Settings > Privacy and Security.
- Select FileVault.
- Click Turn On.
- Choose a recovery method (iCloud or passphrase).
- Click Continue.
How to Encrypt a File: Best Practices
However, after you encrypt a file, the work is not over! Encryption and data security are ongoing works. So to excel in file encryption, consider these best practices:
- Use Strong Passwords or Passphrases. Ensure that you use complex, unique passwords or passphrases for your encryption keys. Avoid using easily guessable passwords or those that can be found in dictionaries. Make sure you update your passwords on a regular basis.
- Regularly Update Encryption Software and Protocols. Keep your encryption software and protocols up to date. You will often be prompted to update to the latest version of the software. Don’t say no! Security vulnerabilities are continually discovered and patched by software developers.
- Securely Manage Encryption Keys. Safeguard your encryption keys with utmost care. Store them in a secure location, and never share them openly. This means you should never write your passphrase in a Google Doc or a Post-it note. Consider using a reputable key management system if dealing with multiple keys. Losing or compromising encryption keys can render your encrypted files inaccessible.
Last Words on File Encryption
That’s it for this guide on how to encrypt a file! Hopefully, you now feel capable of securing your digital world.
Was anything unclear? Did we miss out on anything? Let us know at support@mailfence.com.




