What is end-to-end encryption?
End-to-end encryption is a method of securely transmitting data in a way that only the sender and recipient can read the actual message by encrypting it on the sender’s end and decrypting it on the recipient’s.
Any third party, like a malicious actor, that tries to access or tamper with the data as it travels from one end (sender) to the other (recipient) will be unable to do so without the right decryption key.
End-to-end email encryption provides the highest level of confidentiality and protection for your email communication. Let’s read this article to learn how it works.
How does end-to-end encryption work?
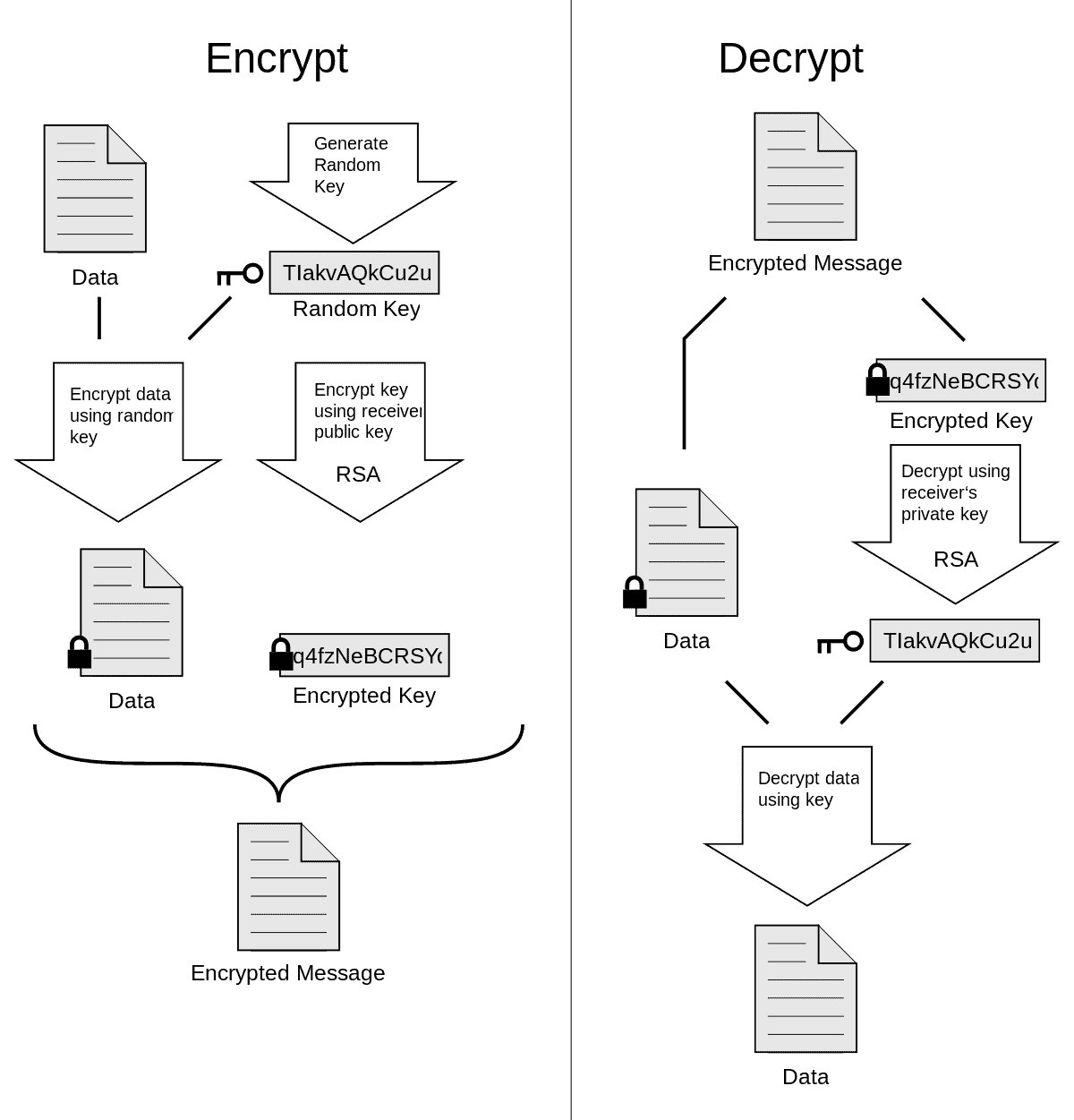
End-to-end encryption requires both the sender and recipient to have a pair of cryptographic keys. There is one private key and one public key. The sender encrypts the message locally on his device using the recipient’s public key. The recipient decrypts it on his device using his private key. This method of encryption is called asymmetric encryption.
The process works as follows:
- Alice (sender) and Bob (recipient) both generate their key pairs and share their public keys with each other. They keep their private key ‘private’ as the name suggests. You only need to generate your keys once when creating an encrypted email account.
- Alice encrypts the message using Bob’s public key on her device and sends it to Bob.
- Bob receives the encrypted message on his device and decrypts it using his private key.
With real end-to-end encryption, also called “client-side encryption” or “zero access”, encryption and decryption happen on the users’ devices. End-to-end encryption thus prevents any intermediary from reading user data and guarantees the confidentiality of the data much more than SSL/TLS or STARTTLS.
How to send an end-to-end encrypted email using Mailfence
- First, generate your keypair, and import the public key of your recipient as described here. You can also import keys via email, meeting in person, …
- Then compose a mail and choose the ‘Sign, Encrypt & Send” option as described below.
- Enter your passphrase and confirm.
- Done.
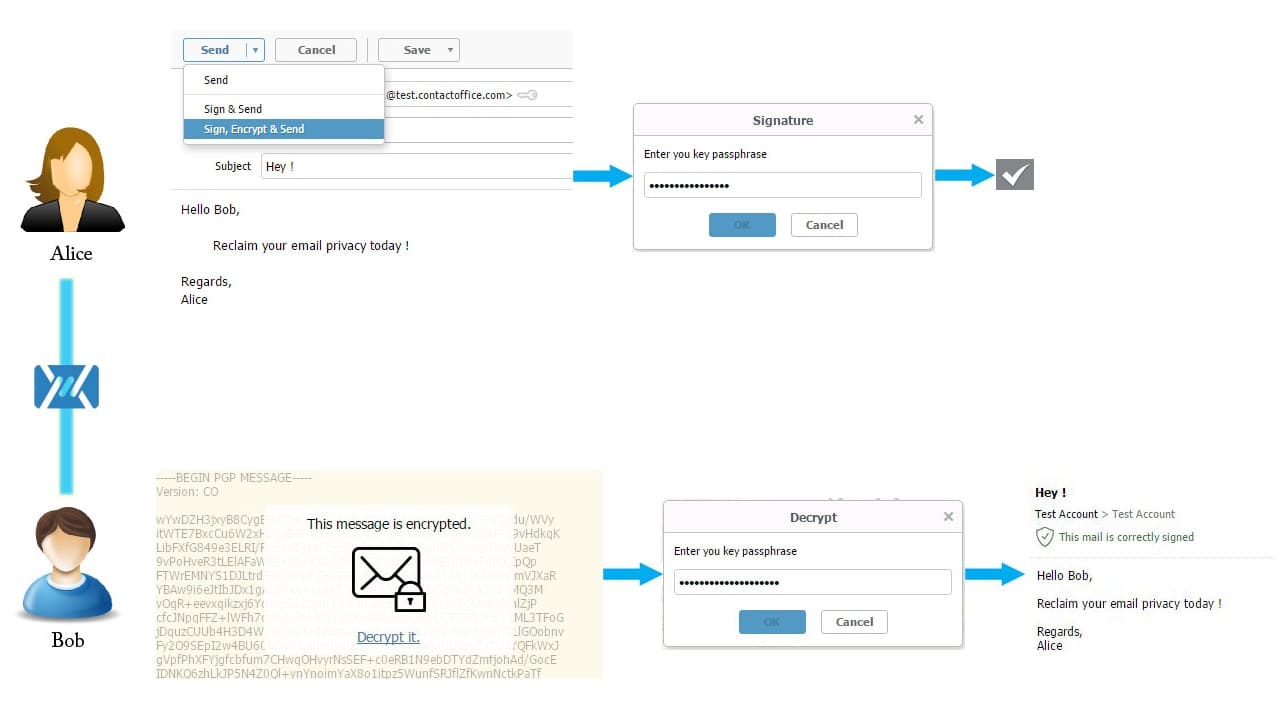
Yes, Mailfence makes end-to-end encryption super easy on email! No plugins, no key management in separate key stores,…
It is just like any other webmail service, but secure and private. Easy, fast, and very convenient for everyone who values their privacy.
Advantages of E2EE
End-to-end encryption has the following advantages:
- Privacy: Only the intended recipient who holds the private key can decrypt the message. E2EE protects you, among other things, from threats of hackers taking hold of the data transfer by eavesdropping on Wi-Fi or other channels.
- More security and authenticity: End-to-end encryption can be combined with digital signatures. A digitally signed and encrypted email proves that the sender is indeed the ‘true’ sender of the message. It also protects against tampering with the message while in transit.
- Say NO to mass-surveillance : End-to-end encryption protects your messages against mass-surveillance and Big Tech. Check out the strong case for encryption article by one of the Mailfence founders.
What does it protect you against?
E2EE will protect your data from two cybersecurity threats:
- Prying eyes. Since only the sender has the original (unencrypted) and the intended recipient has the private key to decrypt the message, any third party that manages to intercept the message in transit will not be able to read the encrypted message (it will be illegible).
- Altering the message. Even if someone intercepts the message, they still can’t tamper with it without discovery, as E2EE protects against such attempts.
What does it not protect?
Despite end-to-end encryption being considered one of the most powerful cybersecurity solutions, there are still things that it cannot protect.
These include:
- Compromised end-points. End-to-end encryption is only as strong as its end points. If, for instance, the sender’s device is compromised, the hacker can get the original message.
- Metadata. Metadata is the information about the message, such as the date and time of sending. Unfortunately, E2EE does not protect metadata, giving the malicious actor some valuable information they could potentially use.
How is end-to-end encryption different from encryption in transit?
To better understand what end-to-end encryption is, we must first understand what is not end-to-end encryption and how E2EE differs from encryption in transit.
- SSL/TLS – When you visit https://www.gmail.com, the HTTPS in front of the URL denotes that SSL/TLS protocol has been used to encrypt the data transferred between your computer and the Gmail servers. This protocol is much more secure than HTTP (without “S” = not secure). Most websites adopted SSL/TLS to protect themselves against malicious intermediaries. The downside to relying solely on HTTPS, is that data is only encrypted between your device and the Gmail servers. Gmail has the keys to decrypt that data.
- SMTP over TLS (STARTTLS) – Let’s take the case of a Yahoo mail user that sends an email to a Gmail user. When you send an email with SMTP over TLS between these two mail services, the message between the two servers is encrypted. Consequently, on the condition that the recipient server also supports SMTP over TLS (which Gmail does). Using STARTTLS is good practice, however several attempts are made to ‘portray’ this as the ultimate email security and privacy solution. In our opinion, STARTTLS is not good enough since both the sending and receiving servers have access to the message content. Moreover, not all receiving servers support STARTTLS.
Conclusion
End-to-end encryption has existed for decades. So why isn’t it more common? There are a few reasons:
First, mainstream providers do not support end-to-end encryption, as their business model often depends on advertising and selling user data. Secondly, our governments want to be able to keep a check on our communications (read why backdoor encryption does not work). Last but not least, end-to-end encryption has traditionally been hard to implement and difficult to use and understand. When evaluating email providers, understanding how they implement encryption is critical. Learn more about choosing secure business email hosting for your company or how to implement email encryption for your small business.
Yet, despite all these, end-to-end encryption remains the most secure way to protect your sensitive data from prying eyes and malicious actors, and Mailfence is there to help you out!
See also:
Secure email: Why end-to-end encryption is at the heart of it, OpenPGP encryption best practices, Symmetric vs asymmetric encryption, Password encrypted messages
Subscribe for free and join the fight for online privacy and digital freedom.




