Email security for small business protects your company’s communications from cyberattacks, data breaches, and unauthorised access. Small businesses face the same email threats as large corporations, but often lack dedicated IT resources to defend against them.
This guide shares practical email security measures specifically designed for businesses with 5–50 employees. You’ll learn about the threats targeting your inbox, how encryption and authentication work, and actionable steps to protect your business communications today.
Looking for an all-in-one solution? Mailfence for Business combines secure email with secure documents, calendars, and contacts – everything your team needs in one privacy-focused platform.
Mailfence — Your secure Productivity Suite
Reclaim your Privacy with
- Messages
- Calendars
- Documents
- Groups
What is email security for small business?
Email security for small business includes all measures protecting your email communications from unauthorised access, data breaches, and cyberattacks. It combines technology solutions with smart practices to keep your messages, attachments, and contact information safe.
Think of it as a digital vault for your business conversations. Just as you lock your office door, email security locks your digital communications. This protection extends beyond just messages – it covers everything from client lists to financial documents you send via email.
Small businesses need specialised email security because they face unique challenges. They handle sensitive data like larger companies but without their resources. One successful phishing attack can devastate a small business financially and reputationally. The key is finding security solutions that give enterprise-grade protection without enterprise-level difficulty.
Why do small businesses need strong email security?
Small businesses make attractive targets for cybercriminals. They often have weaker defences than large corporations, but still process valuable data. Hackers know this and specifically target smaller organisations.
Consider these realities small businesses are facing today:
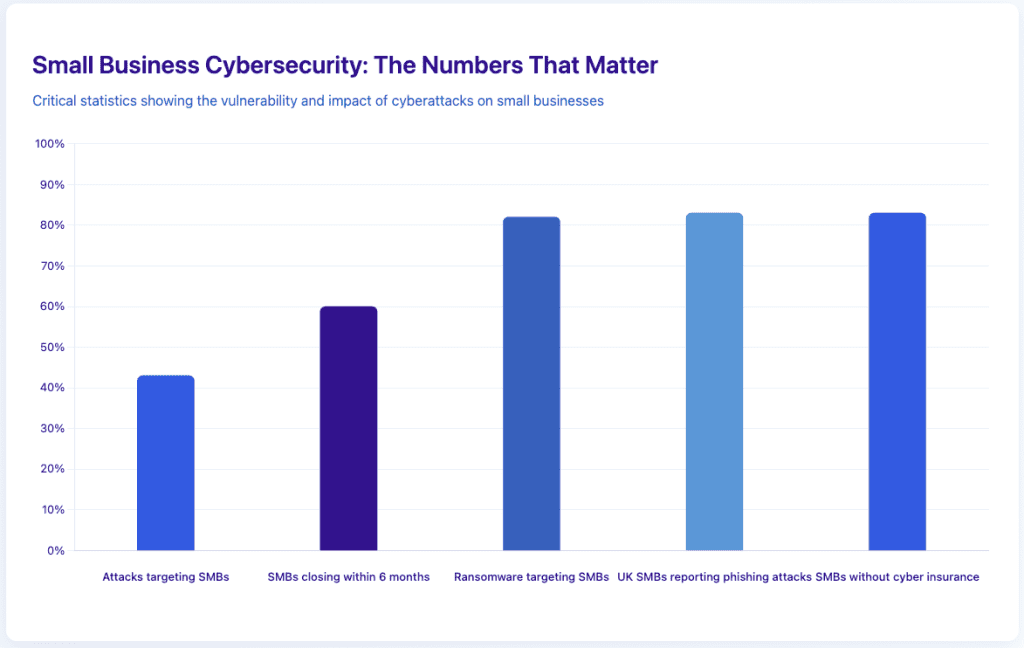
- 43% of cyberattacks target small businesses: Criminals see you as easy prey with valuable data
- 60% of small businesses close within 6 months of a cyberattack: Recovery costs can destroy your business
- Average breach costs small businesses $120,000 to $1.24 million: Most small businesses can’t absorb this loss
- 83% of UK SMBs that suffered cyberattacks cite phishing: Email remains the primary attack vector, with phishing attempts increasing 13% year-over-year
“Your business email contains everything criminals want. Customer payment information, supplier contracts, employee records, and intellectual property all flow through email. Without proper security, you’re gambling with your company’s future.” – Patrick De Schutter, Co-founder Mailfence
What are the main email threats facing small businesses?
Understanding specific threats helps you defend against them effectively. Small businesses face several common email-based attacks that you should recognise and prepare for.
Phishing attacks
Phishing remains the most dangerous email threat for small businesses. Criminals send fake emails that look legitimate, tricking employees into revealing passwords or financial information. These attacks grow increasingly sophisticated each year.
Modern phishing uses social engineering and publicly available information. Attackers research your business on social media, then craft personalised messages. They might impersonate vendors, customers, or even your CEO.
Business email compromise (BEC)
BEC attacks specifically target businesses by impersonating executives or suppliers. Criminals hack or spoof email accounts, then request urgent wire transfers or sensitive data. Small businesses lose billions annually to these scams.
These attacks succeed because they exploit trust and authority. When an email appears to come from your boss requesting immediate action, employees often comply without verification.
Malware and ransomware
Malicious attachments remain a primary infection vector for small businesses. One employee clicking a fake invoice can encrypt your entire network. Ransomware attacks paralyse operations until you pay criminals for decryption keys.
Recovery costs extend far beyond ransom payments. You lose productivity during downtime, pay for system restoration, and potentially face regulatory penalties for data exposure. Small businesses experience an average of 24 days downtime after ransomware attacks1.
Data breaches through email
Email accounts store years of sensitive communications. When hackers gain access, they harvest customer data, financial records, and trade secrets. This stolen information fuels identity theft, corporate espionage, and further attacks.
Small businesses often discover breaches months after they occur. By then, criminals have sold your data on the dark web, and the damage becomes irreversible:

How does email security for small businesses work?
Email security creates multiple protection layers between your messages and potential threats. Each layer serves a specific purpose, working together to block attacks while letting legitimate messages through.
Encryption scrambles your email content so only intended recipients can read it. When you send an encrypted email, it becomes unreadable gibberish to anyone who intercepts it. The recipient’s email system decrypts the message using a unique key.
Authentication protocols verify that emails actually come from who they claim. SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records tell receiving servers whether messages from your domain are legitimate. This stops criminals from impersonating your business.
Spam and malware filters scan incoming messages for threats. They check sender reputation, analyse message content, and examine attachments for viruses. Advanced filters use AI to detect sophisticated phishing attempts.
Access controls limit who can view your email account. Multifactor authentication requires both a password and a second verification method. This stops hackers even if they steal your password.
Email security for small business best practices
Building strong email security requires implementing practical measures that your team will actually follow. These best practices balance security effectiveness with operational efficiency for businesses with 5–50 employees. Address these basics first – they eliminate the most common attack vectors. Then systematically implement the best practices outlined in Business Email Security: Fundamentals and Best Practices for 2026, prioritising based on your specific risks. And speaking of specific risks: We have a great Email Security and Privacy Course for anyone wanting to dive even deeper.
1. Quick security assessment checklist
Before implementing new measures, conduct this 30-minute audit to identify immediate vulnerabilities:
- Check password strength across all accounts
- Remove former employee access immediately
- Verify two-factor authentication on admin accounts
- Review shared account passwords (info@, support@, sales@)
Addressing these basics eliminates the most common entry points for attackers.
2. Implement strong password policies
Require passwords at least 12 characters long. Consider passphrases – four random words are easier to remember and stronger than complicated combinations.
Deploy a password manager like Bitwarden. Start with administrative and financial teams, then expand after initial success. For shared accounts, store credentials securely and rotate when employees leave.
3. Set up email authentication standards
Configure SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records to prevent domain spoofing. For other providers, test your configuration at mail-tester.com – scores above 7/10 indicate good authentication.
4. Enable appropriate encryption
Implement tiered encryption:
- Standard: TLS for all connections (automatic with modern providers)
- Enhanced: End-to-end encryption for financial documents, employee data, contracts, and strategic plans
5. Train your team on security awareness
Weekly briefings: Share real attack examples from your industry. Show actual phishing emails and warning signs.
Simulated tests: Conduct monthly phishing simulations. Immediate training for those who click suspicious links builds better habits.
Clear reporting: Designate a security point person. Encourage questioning suspicious requests.
6. Establish verification procedures
Financial transactions:
- Under $1,000: Email approval
- $1,000-$5,000: Phone verification
- Over $5,000: Two-person approval
- New vendors: Always verify banking by phone
These procedures stop most business email compromise attempts.
7. Implement access controls
Create four access levels:
- Administrative (owners, IT)
- Financial (accounting, payroll)
- Standard (regular employees)
- Limited (contractors, temps)
Enable multifactor authentication starting with high-risk accounts. Monitor for unusual login locations or mass deletions.
8. Regular security maintenance
Schedule quarterly reviews of passwords, permissions, updates, and backups. Test incident response annually. Document lessons learned and update procedures accordingly.
Which email security features matter most?
Not all security features deliver equal value for small businesses. Focus on capabilities that give maximum protection without overwhelming your team.
End-to-end encryption
End-to-end encryption ensures only you and your recipient can read messages. Even if hackers intercept emails or breach servers, they can’t decrypt your communications. This protection proves essential for confidential business discussions.
Mailfence offers built-in end-to-end encryption using OpenPGP standards. Your messages stay encrypted from composition through delivery, protecting them at every stage. The key for small businesses is making encryption simple enough that employees actually use it for sensitive communications.
Two-factor authentication (2FA)
2FA adds a second verification step beyond passwords. Even if criminals steal login credentials, they can’t access accounts without the second factor. This simple feature blocks most unauthorised access attempts.
Advanced spam filtering
Modern spam filters use machine learning to detect threats traditional rules miss. They analyse sender behaviour, message patterns, and content anomalies. This intelligence adapts as attack methods evolve.
Quality filters reduce false positives that block legitimate messages. You need protection that stops threats without disrupting business communications.
Attachment scanning
Every attachment poses potential risk. Effective scanning examines files for malware, suspicious scripts, and unusual behaviour. Some systems sandbox attachments, testing them in isolated environments before delivery.
Look for scanners that check compressed files and embedded macros. Criminals often hide malware several layers deep to evade basic detection.
What are the best email platforms for small business?
Choosing the right secure email provider requires balancing security, usability, and cost for your specific business size and needs. Not all “secure” email solutions offer the same level of protection – some provide end-to-end encryption that keeps messages private even from your email host, while others only encrypt data in transit, leaving your provider with full access to your communications.
This comprehensive comparison guide evaluates 7 major secure business email providers across encryption strength, privacy protections, productivity features, and pricing.
Here’s how the top providers compare:
Mailfence: Integrated security and productivity suite (email, calendar, documents) under Belgian GDPR. Automatic encryption without IT expertise. From €2.50/user/month.
Proton Mail: Swiss privacy law with open-source transparency. Strongest legal protection but less integrated productivity tools than Mailfence.
Tuta: German encryption at €3/user/month. Budget-friendly with basic email and calendar, but minimal collaboration features.
Microsoft 365: Enterprise features with Office integration. Requires 1–2 days setup and lacks end-to-end encryption – Microsoft can access your messages.
Google Workspace: Familiar interface but no end-to-end encryption. Google scans email content and stores data under US jurisdiction.
Zoho Mail: Budget option at €0.92/user/month with basic security. No end-to-end encryption; allows data collection for analytics.
FastMail: Technical users’ choice with customizable management under Australian law. Policy-based privacy, not encryption. Australian privacy law is weak, offering less protection compared to the EU’s GDPR data protection standards, so privacy largely depends on company policies rather than robust legal safeguards.
Email marketing platforms, such as Mailchimp, Brevo and MailerLite, on the other hand serve a different purpose than secure business email hosting – they’re designed for campaigns, newsletters, and bulk communications rather than day-to-day business correspondence and data protection.
Which free email security options work for small business?
Budget constraints don’t excuse poor email security. Several free options give basic protection while you grow, though understanding their limitations is crucial.
Gmail and Outlook.com offer baseline security, including spam filtering and 2FA. However, they lack end-to-end encryption and analyse messages for advertising purposes, creating privacy concerns.
Mailfence offers a free plan including secure email and basic productivity tools. While storage is limited, you get true privacy without ad scanning – useful for testing before committing to paid plans.
Zoho Mail offers TLS encryption, two-factor authentication, anti-spam, and antivirus protection. The free plan supports up to 5 users and is suitable for small businesses needing basic security and productivity tools.
The reality for growing businesses: Free plans become costly through lost productivity and migration pain. By employee number five, investing $50 monthly in proper email security becomes economical compared to potential breach costs.
Key takeaways: email security for small business
1. Small businesses face targeted threats: Criminals specifically exploit smaller companies’ limited IT resources.
2. Layered protection works best: Combine technology solutions with employee training and clear procedures.
3. Start with security fundamentals: Basic protections implemented well beat complicated systems poorly maintained.
4. Choose appropriate tools and platforms designed for 5-50 person teams, not enterprise solutions.
5. Balance security with usability: Protection only works if your team actually follows the procedures.
6. Regular maintenance is essential: Schedule quarterly reviews to maintain security effectiveness.
Final thoughts on small business email security
Email security for small businesses requires finding the right balance between protection and practicality. Your 5–50 person team needs security that works in your operational constraints while giving real protection against modern threats.
Start by conducting the 30-minute security assessment to identify immediate vulnerabilities. Address these basics first – they eliminate the most common attack vectors. Then systematically implement these best practices.
Consider platforms built specifically for small business email security needs. Mailfence exemplifies this approach, combining enterprise-grade protection with the simplicity small teams require. You get encryption, secure file sharing, and integrated productivity tools without difficulty or privacy compromises.
Want more insights on protecting your business communications? Follow our newsletter for privacy-focused content that helps small businesses stay secure in an evolving threat landscape.
Get the latest privacy news in your inbox
Sign up to the Mailfence Newsletter.
- Source: Statista (cited in NinjaOne 2025, PurpleSec 2025, Spacelift 2025) ↩︎