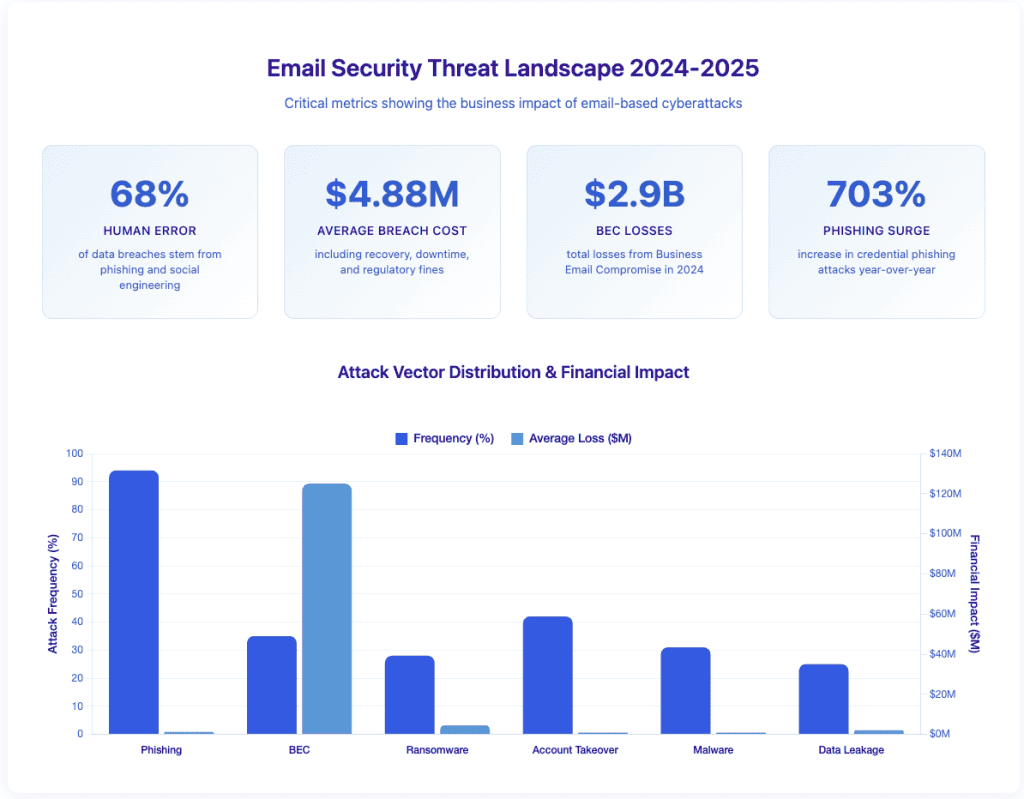
Email remains the primary entry point for cyberattacks. In 2024, 68% of data breaches stemmed from human error, mainly from phishing scams1. One clicked link can expose customer data, financial records, and intellectual property. The average data breach costs $4.88 million2, whilst Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks caused $2.9 billion in losses3. Credential phishing surged by 703% in 20244, and employees face at least one advanced phishing attack per mailbox every week.
The good news? Protection doesn’t require enterprise-level resources. Enable MFA immediately, put email encryption in place, train your team to recognise threats, and use authentication protocols (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) to verify sender identity. These fundamental steps dramatically reduce your risk.
Mailfence’s Productivity Suite offers end-to-end encryption, built-in security features, and full collaboration tools – secure email, calendar, documents, and contacts in one privacy-focused platform.
Mailfence — Your secure Productivity Suite
Reclaim your Privacy with
- Messages
- Calendars
- Documents
- Groups
Start here: top 3 email security practices
If you do nothing else, start with these three actions:
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Add an extra security layer with an authenticator app or hardware key. Avoid SMS-based MFA.
- Encrypt emails and attachments: Use end-to-end encryption like PGP or S/MIME. Never send sensitive data unprotected.
- Train employees on phishing: Run phishing simulations. Teach employees to verify senders and report suspicious emails.
These three practices deliver the highest ROI for your security investment and block the majority of common attacks.
What is business email security?
Your emails carry contracts worth millions, customer credit cards, and trade secrets. Right now, they’re probably travelling across the internet as readable as a postcard. Business email security changes that.
Modern email security addresses these vulnerabilities through multiple layers. Encryption scrambles message content, so only intended recipients can read it. Authentication protocols verify sender identity to prevent impersonation. Threat detection systems scan for malicious links and attachments before they reach your inbox. Access controls stop unauthorised users from compromising accounts.
These protections work together because no single solution catches every threat. According to ENISA’s Threat Landscape Report 2024, email remains the initial attack vector in 41% of security incidents. Cybercriminals constantly adapt, finding creative ways to bypass basic security. Your email security strategy must evolve with them.
Why your business needs email security
BEC attacks don’t require sophisticated hacking skills – attackers simply trick employees into wiring money or sharing credentials. Employees face at least one advanced phishing attack per mailbox weekly5.
Social media adds another layer of risk. It accounts for 30.5% of all phishing attacks6, with scammers using fake LinkedIn profiles and Facebook messages to steal credentials.
Remote work expands your attack surface. Employees access email from personal devices, home networks, and coffee shops. Each access point creates vulnerabilities. Traditional perimeter security doesn’t work when your perimeter includes hundreds of remote locations.
Small businesses aren’t exempt. 43% of cyberattacks target small companies specifically7. Attackers know smaller businesses often lack dedicated security teams and assume they’re easier targets. You can’t afford to skip email security for small business just because you’re not a Fortune 500 company.
Regulatory fines multiply costs. GDPR violations cost up to 4% of annual revenue or €20 million, whichever is higher8. HIPAA breaches carry penalties reaching $2 million per violation9. Beyond fines, you face legal liability, notification requirements, and forensic investigation costs averaging $2.36 million10.
Interested in email security for larger organisations? Head on over to Enterprise Email Security: Best Practices.
The Hidden Costs Beyond Money
Reputational damage compounds financial losses. When customer data leaks, clients lose trust – often permanently. A Ponemon Institute study found 65% of customers lose confidence in organisations after a breach. Recovery takes years.
Common business email security threats
| Threat | Description | Impact |
| Phishing | Deceptive emails trick recipients into clicking malicious links or sharing credentials with professional formatting and urgent language. | 94% of malware delivery (Verizon DBIR). Leads to account compromise, data theft, and lateral network attacks. |
| Business Email Compromise (BEC) | Attackers impersonate executives or trusted partners to authorise fraudulent wire transfers. No malware – just exploits trust. | 703% increase in 2024 (Abnormal Security). Average loss exceeds $125,000 per incident. |
| Ransomware | Malware delivered via email attachments encrypts your files and demands payment for the decryption key. | Average cost $4.54 million including downtime, recovery, and regulatory investigations (Sophos 2024). |
| Account takeover | Attackers gain access through stolen credentials, then monitor communications, steal data, and send malicious emails from trusted accounts. | Bypasses spam filters. Enables attacks on other employees, customers, and partners. |
| Malware distribution | Email delivers viruses, trojans, spyware, and keyloggers through attachments or links to infected websites. | Steals credentials, monitors activity, creates backdoors, damages systems. |
| Spoofing and impersonation | Attackers forge sender addresses or register similar domains to make messages appear from legitimate sources. | Creates urgency, reduces suspicion, enables social engineering attacks. |
| Data leakage | Sensitive information leaves your organisation through intentional exfiltration or accidental sharing with wrong recipients. | Exposes customer lists, intellectual property, financial records. Can’t recall sent messages. |
Essential business email security best practices
1. Train employees on cybersecurity awareness
Hackers exploit human error to bypass security. Employees must learn to slow down, verify, and report suspicious emails before acting.
Cybersecurity training should focus on recognizing threats, questioning unusual requests, and building safe email habits.
Teach employees to identify phishing:
- Urgent requests demanding passwords or financial actions (“Your account will be closed in 24 hours”)
- Email addresses that closely mimic legitimate senders (arnazon.com instead of amazon.com)
- Links that hide real destinations behind misleading text (hover to reveal bit.ly/x7g9 instead of microsoft.com)
Use real phishing examples in training. Break down how attackers manipulate emotions and language to trick recipients. Highlight red flags – generic greetings, urgent language, suspicious sender addresses, unexpected attachments, requests to verify credentials. Have employees practise identifying phishing in simulated exercises.
Explain social engineering tactics. Attackers exploit trust, authority, and urgency. They impersonate executives requesting immediate action. They pretend to be IT support needing credentials to fix problems. They create artificial deadlines to bypass normal verification processes.
Run phishing simulations quarterly
Send fake phishing emails to test employee vigilance. When someone clicks, offer immediate education rather than punishment. The goal isn’t to catch failures – it’s to build instincts that prevent real breaches. Companies using regular simulations see 87% fewer successful phishing attacks11.
2. Use strong, unique passwords
Weak or reused passwords enable brute force attacks, credential stuffing, and unauthorised access. Once hackers steal one password, they try it everywhere – email, banking, work systems. The average person reuses passwords across 14 accounts12.
Create long, strong passwords
Use at least 16 characters combining uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols. Avoid predictable choices like “Password123” or personal details such as birthdays. According to Hive Systems 2024 research, an 8-character password takes 5 minutes to crack, whilst a 16-character password takes 34,000 years.
Never reuse passwords
Using the same password across multiple accounts is a security disaster waiting to happen.
Use password managers
No one can memorise dozens of strong passwords, and writing them down creates risks. A LastPass study found organisations using password managers experience 50% fewer password-related security incidents.
Put password managers in place organisation-wide. Tools like Bitwarden for Business, 1Password for Teams, or LastPass Enterprise offer centralised management with secure sharing for team credentials. These generate, store, and autofill strong passwords so employees don’t have to remember dozens of complex credentials.
3. Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA)
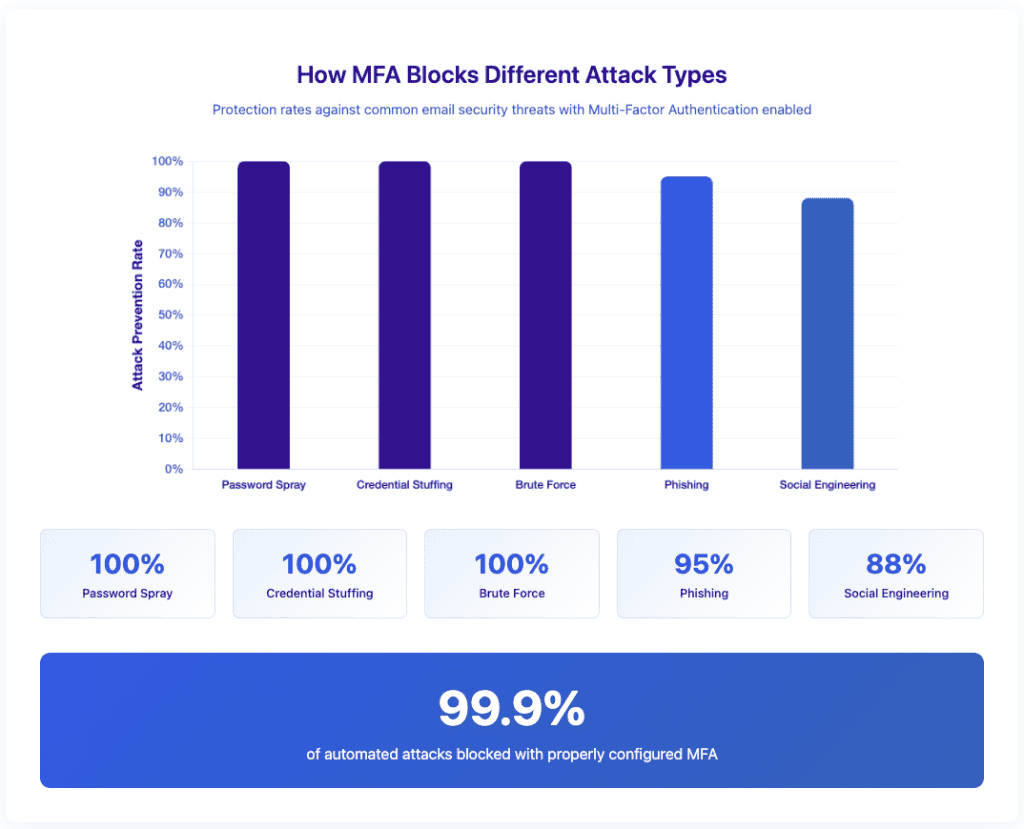
MFA blocks account takeover even when passwords are compromised. Microsoft reports that MFA blocks 99.9% of automated account compromise attempts13. Yet only 57% of businesses have it enabled globally14.
Add a second layer of protection
A stolen password shouldn’t be enough to access an account. Require employees to verify access with:
- Biometrics (fingerprint or facial recognition)
- Authenticator apps (Google Authenticator, Authy, Microsoft Authenticator)
- Hardware security keys (YubiKey, Titan Security Key)
Avoid SMS codes – they can be intercepted through SIM swapping attacks.
Make MFA a company policy – not an option
Require MFA for all employees. Enforce it across email accounts, cloud platforms, and internal systems.
Mailfence offers built-in Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) for stronger account protection. Activate it in settings and choose a preferred authentication method.
Train employees to spot MFA bypass attempts
Hackers know MFA blocks most attacks, so they try to trick employees into revealing codes. If an email or call asks for a verification code, it’s a scam. No legitimate service will ever ask for your MFA code.
4. Encrypt emails and secure communication
Send an unencrypted email with customer data and you might as well post it on LinkedIn. Every router, server, and network admin between you and your recipient can read it.
“Security is more than encryption, of course. But encryption is a critical component of security. You use strong encryption every day, and our Internet-laced world would be a far riskier place if you didn’t.” – Bruce Schneier, Cryptography Expert
Use end-to-end encryption (E2EE)
Basic encryption only secures emails whilst they travel. Once a message reaches the server, it becomes vulnerable. End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) locks emails from the moment they’re sent until the recipient decrypts them. No one else – email providers, hackers, or government agencies – can read them.
Transport Layer Security (TLS) encrypts the connection between email servers, protecting messages in transit. However, TLS only secures the journey – not the message itself. Email providers can still read message content, and encryption stops at each server hop.
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) locks message content so only the intended recipient can decrypt it. According to Internet Engineering Task Force RFC 4880, properly implemented OpenPGP encryption would take longer than the age of the universe to crack with current technology.
Encrypt emails with Mailfence’s OpenPGP security
Mailfence offers OpenPGP encryption for businesses handling financial data, legal documents, or sensitive client communications. The system works with a public-private key system.
5. Block email spoofing with SPF, DKIM, and DMARC
Cybercriminals forge email addresses to trick recipients into opening harmful messages. Without proper security protocols, attackers can impersonate your domain and send fraudulent emails that look real.
Stop them by setting up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. These protocols verify sender identities, protect message integrity, and block phishing attempts.
SPF: Verify sending mail servers
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) tells email servers which mail sources can send messages for your domain. Without SPF, anyone can send emails appearing to come from your company.
DKIM: Protect email integrity
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) adds a digital signature to emails, proving they haven’t been altered in transit. Without DKIM, attackers can modify messages and insert harmful links before they reach the recipient.
DMARC: Align SPF and DKIM for stronger protection
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) works with SPF and DKIM to block spoofed emails. It tells receiving servers how to handle messages that fail authentication and provides reports on unauthorized attempts.
Mailfence automatically validates SPF, DKIM, and DMARC for incoming emails. It flags, quarantines, or rejects messages that fail authentication, preventing phishing emails from reaching employees. Businesses can customize validation settings to enforce stricter security policies.
6. Deploy an email security solution
Hackers rely on email to spread malware, steal credentials, and launch phishing attacks. Without protection, your business stays exposed to threats that can shut down operations or leak sensitive data. You need an enterprise-grade email security solution that blocks these attacks before they reach your inbox.
Secure your inbox with a Secure Email Gateway (SEG)
A Secure Email Gateway (SEG) filters threats before they enter your network. Set up an SEG to:
- Stop phishing and malware before they reach employees
- Prevent Business Email Compromise (BEC) scams
- Enforce compliance using encryption and Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools
Block phishing, spam, and email fraud
Spam filters alone are not enough. Sophisticated attackers use advanced evasion techniques. Deploy enterprise-grade solutions like Mimecast or Proofpoint to analyze email patterns, detect suspicious links, and quarantine high-risk messages in real time.
Train employees to recognize and report suspicious emails rather than interacting with them.
Encrypt emails to prevent unauthorized access
Hackers intercept unprotected emails to steal sensitive data. Encrypt all business emails to block unauthorized access.
Mailfence’s TLS Encryption secures emails with Transport Layer Security (TLS), preventing outsiders from reading messages. Businesses handling financial, legal, or customer data should adopt such encrypted email infrastructures.
7. Prevent unauthorised access
Cybercriminals look for weak spots in business email security. Don’t give them an opening. Lock down email access, track login attempts, and enforce encryption to block unauthorized entry.
Restrict email access to approved devices
Require email access only from company-managed devices with:
- Full-disk encryption (BitLocker, FileVault, LUKS)
- Automatic screen lock after 10 minutes
- Remote wipe capabilities
- Updated antivirus software
Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions enforce these policies automatically. Companies using MDM report 67% fewer device-related incidents (Aberdeen Group 2024).
Restrict logins to trusted locations
If your business operates only in Europe, block login attempts from Asia, Africa, and the Americas. Microsoft Azure AD reports that geographic restrictions prevent 89% of credential stuffing attacks.
Monitor logins and enforce auto-logout
Track login activity in real time. Configure alerts for:
- Login attempts from new devices
- Access from unusual locations
- Multiple failed login attempts
- Logins outside business hours
Mailfence forces all connections – IMAP, SMTP, and POP – through SSL/TLS encryption, blocking hackers from intercepting login credentials.
8. Improve endpoint & email security hygiene
Cybercriminals target outdated software, unprotected endpoints, and weak email security. Stop giving them an entry point. Strengthen your defenses with these steps.
- Set all software, operating systems, and antivirus programs to update automatically.
- Use a centralized patch management system to push updates efficiently across all devices.
- Regularly review security logs to detect threats early and act before they escalate.
Use email scanning tools to block malicious attachments
Email attachments remain a common malware delivery method. Protect your inbox by:
- Using sandboxing technology to safely test unknown files before allowing downloads.
- Deploying an email security gateway to filter incoming attachments.
- Automatically blocking executable files and suspicious formats.
Mailfence’s Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) encrypts each email session separately, making stolen keys useless for accessing past conversations.
9. Avoid public Wi-Fi for email communication
Public Wi-Fi puts business emails at risk. Hackers can intercept your login credentials, read your messages, and steal sensitive data.
Airports, coffee shops, and hotels offer free internet, but that convenience comes at a cost – exposed information. Never assume a public network is safe, even if it requires a password.
Public Wi-Fi risks:
- Data interception & Man-in-the-Middle attacks: Hackers can position themselves between your device and the Wi-Fi hotspot, intercepting sensitive information such as passwords, emails, and business credentials. This allows them to eavesdrop on your communication or hijack sessions.
- Evil twin & rogue hotspots: Cybercriminals create fake Wi-Fi networks that mimic legitimate ones, tricking users into connecting. These “evil twin” hotspots can then monitor or manipulate all traffic.
- Malware distribution: Hackers can exploit unsecured networks to inject malware into devices, including spyware, ransomware, or other malicious software.
- Packet sniffing & eavesdropping: Cybercriminals use specialized tools to monitor unencrypted data transmitted over public Wi-Fi, capturing login credentials, personal messages, or confidential business information.
Best practices for securing public Wi-Fi use
- Avoid accessing sensitive information (banking, confidential emails) on public networks. Use mobile data or wait until you’re on a secure, trusted network.
- Use a VPN to encrypt your internet traffic and prevent eavesdropping.
- Enable firewall protection to detect and block unauthorized access.
- Turn off automatic Wi-Fi connections and verify network names before joining to avoid fake hotspots.
- Use two-factor authentication (2FA) for all critical accounts to add an extra security layer.
- Employ secure email platforms like Mailfence that enforce HTTPS and TLS encryption, such as Mailfence’s HSTS Protection, to protect email content.
10. Put Data Loss Prevention (DLP) in place
Data Loss Prevention tools prevent sensitive information from leaving your organisation.
How DLP works:
- Pattern matching: Identifies credit card numbers, National Insurance numbers, passport numbers
- Keyword scanning: Flags “confidential,” “proprietary,” “internal only”
- Contextual analysis: Considers sender, recipient, and data classification
- Machine learning: Learns normal behaviour patterns and flags anomalies
Start with monitoring to reduce false positives.
11. Regularly back up email data
Losing emails disrupts communication, exposes data, and causes major business setbacks. Automate backups to prevent email loss.
Backup best practices:
- Automate email backups by scheduling automatic backups instead of relying on manual exports to ensure consistency and reduce the risk of human error.
- Store backups in multiple secure locations using a mix of local storage and encrypted cloud storage to protect against data loss. For example, follow the 3-2-1 rule: keep 3 copies of your data, use 2 different storage types, and store 1 copy off-site.
- Use case: Mailfence’s secure email backup allows businesses to export and securely store emails on external encrypted storage devices. Its automated backup system keeps important messages protected and easily recoverable.
- Test backup integrity regularly by performing routine tests to ensure backups can be restored quickly when needed.
- Use encrypted storage solutions to protect your backup files with encryption (e.g., AES-256) and strong access controls to prevent unauthorized access.
Key takeaways: business email security
Email remains the primary attack vector targeting businesses, responsible for 68% of cyberattacks. Protecting your communications isn’t optional – it’s essential for business survival.
Multi-factor authentication blocks most account compromises by requiring verification beyond passwords. Enable MFA immediately for all email accounts, especially administrators and executives.
Email encryption protects message confidentiality from interception and unauthorized access. End-to-end encryption with OpenPGP or S/MIME ensures only intended recipients can read sensitive communications.
Authentication protocols prevent impersonation by verifying sender identity. Implement SPF, DKIM, and DMARC together to stop attackers from spoofing your domain and improve email deliverability.
Employee training transforms your team from vulnerability to defense. Regular security awareness education teaches threat recognition, reducing successful phishing and social engineering attacks.
Layered security provides the best protection because no single tool stops every threat. Combine technical controls (filtering, encryption, authentication) with human-focused strategies (training, policies) for comprehensive coverage.
Final thoughts on business email security
Email security protects more than just messages. It safeguards customer trust, business reputation, and operational continuity. The threats are real and growing, but protection doesn’t require enterprise budgets or dedicated security teams.
Start with high-impact fundamentals – enable MFA, implement authentication protocols, train your employees. These steps dramatically improve your security posture within weeks. Build from there with encryption, advanced filtering, and comprehensive monitoring.
Think of email security as ongoing maintenance rather than a completed project. Threats evolve constantly, requiring your defenses to evolve with them. Regular training updates, security monitoring, and prompt patching keep protections effective.
Ready to strengthen your email security? Mailfence provides the tools you need with the privacy you deserve. Start with secure, encrypted communications that keep your business data confidential. If you want to hear more privacy-related content, give our newsletter a follow!
Get the latest privacy news in your inbox
Sign up to the Mailfence Newsletter.
Sources
- IBM Security Cost of Data Breach Report 2024 ↩︎
- Ponemon Institute 2024 ↩︎
- FBI IC3 Report 2024 ↩︎
- Abnormal Security Threat Report ↩︎
- Barracuda Networks 2024 ↩︎
- Proofpoint State of the Phish 2024 ↩︎
- Verizon DBIR 2024 ↩︎
- European Data Protection Board 2024 ↩︎
- US Department of Health and Human Services ↩︎
- NetDiligence Cyber Claims Study 2024 ↩︎
- SANS Security Awareness Report 2024 ↩︎
- Google Security Survey 2024 ↩︎
- Microsoft Security Intelligence 2024 ↩︎
- Cyber Security Breaches Survey 2024 ↩︎
FAQ about business email security
What is email security?
Email security is the collection of technologies, protocols, and practices that protect email accounts and communications from unauthorised access, data loss, and cyber threats. It encompasses encryption (scrambling messages so only intended recipients can read them), authentication protocols (verifying sender identity), threat detection (scanning for malicious content), and access controls (restricting who can access accounts). Think of it as a multi-layered shield protecting your business communications from the 94% of cyberattacks that start with email (Verizon DBIR 2024).
How does email security work?
Email security works through multiple defensive layers. First, authentication protocols (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) verify that emails actually come from legitimate senders. Next, encryption protects message content during transmission and storage – Transport Layer Security (TLS) secures the connection between servers, whilst end-to-end encryption (like OpenPGP) ensures only recipients can decrypt messages. Machine learning algorithms scan for malicious patterns, sandboxing suspicious attachments in isolated environments before delivery. Multi-factor authentication adds login barriers, requiring additional verification beyond passwords. These layers work together because no single defence catches everything – whilst MFA blocks 99.9% of automated attacks, phishing simulations reduce human error by 87%.
Why is email security important?
Email security is critical because email remains the primary attack vector for 91% of cyberattacks (ENISA 2024). The average data breach costs $4.88 million, with Business Email Compromise alone causing $2.9 billion in losses annually. Beyond financial damage, breaches destroy customer trust – 65% of customers lose confidence after a breach (Ponemon Institute). Regulatory penalties compound the pain: GDPR fines reach 4% of annual revenue, or €20 million. Small businesses aren't exempt – 43% of attacks target them specifically because hackers assume weaker defences. Without email security, one clicked link can expose customer data, intellectual property, and destroy decades of reputation building.
What is the best email for business use?
The best business email solution combines robust security with productivity features. Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace dominate the enterprise market with integrated collaboration tools, but they lack end-to-end encryption by default. For privacy-focused businesses, Mailfence offers OpenPGP encryption, digital signatures, and 2FA built-in, operating under strict European data protection laws. Proton Mail provides similar encryption but with fewer collaboration features. The "best" depends on your priorities: if you handle sensitive data (financial, medical, legal), prioritise end-to-end encryption providers. For general business with strong authentication needs, enterprise platforms with additional security gateways work well. Always ensure your choice includes MFA, encryption options, and DMARC support.
Are business emails secure?
Standard business emails are not secure by default. Most providers use TLS encryption for transmission, but messages remain readable on servers and to providers themselves. Without additional security measures, business emails are vulnerable to interception, account takeover, and phishing. The concerning reality: 68% of breaches stem from human error via email, and employees face weekly phishing attempts. However, business emails become highly secure when properly configured with MFA (blocks 99.9% of automated attacks), end-to-end encryption, SPF/DKIM/DMARC authentication, and regular security training. The key word is "configured" – security features exist but require activation and proper setup.
What is the most secure email for business?
The most secure business email services offer end-to-end encryption, zero-knowledge architecture (where providers cannot read your emails), and comprehensive authentication. Top secure options include: Mailfence (OpenPGP encryption, Belgian privacy laws, integrated collaboration suite), Proton Mail (Swiss privacy protection, open-source encryption), and Tuta (German privacy laws, automatic E2EE). For enterprises requiring advanced threat protection, standard platforms (Microsoft 365, Google Workspace) combined with dedicated security gateways like Mimecast or Proofpoint offer comprehensive protection. The most secure setup isn't just about the provider – it requires enabling all security features, training employees, and maintaining vigilant security practices.
What is Business Email Compromise?
Business Email Compromise (BEC) is a sophisticated scam where criminals impersonate executives, vendors, or trusted partners to trick employees into transferring money or sharing sensitive data. Unlike traditional phishing, BEC attacks don't use malware – they exploit human trust and authority. Attackers research targets extensively, learning communication patterns and timing requests when verification is difficult (CEO travelling, end-of-quarter rushes). Common tactics include fake invoice schemes, CEO fraud (urgent wire transfer requests), and account compromise (using hacked legitimate emails). Prevention requires email authentication protocols, dual approval for transfers, and out-of-band verification for unusual requests.
Who is liable when business emails are hacked?
Liability for email breaches is complex and depends on multiple factors. The business typically bears primary liability for customer data breaches, facing regulatory fines (GDPR, CCPA), lawsuits, and notification costs. However, liability can extend to employees if negligence is proven (ignoring security policies, sharing passwords), third-party vendors with inadequate security, and email providers if they failed to implement promised security measures. Insurance coverage varies – whilst cyber liability policies may cover some costs, they often exclude employee negligence or failure to implement basic security measures. Courts increasingly expect "reasonable security measures" including MFA, encryption, and employee training. The Morrisons case established that companies can be vicariously liable for employee data misuse, even with security measures in place.